Disruptive Technologies- UberX
Task 1: Industry Structure
a) Compare the cost of a standard taxi ride versus a ride with UberX from Deakin University, Burwood campus to the Melbourne Tullamarine airport. Which would you prefer? Explain your answer.
b) Assume that the taxi industry operates in an unregulated market and is characterized by monopolistic competition. Assume also that taxis and Uber are substitutes
(i) Using diagrams, illustrate and discuss the long-run equilibrium of the taxi industry and individual monopolistic competitive taxi companies before and after the introduction of UberX. (Hint: use one diagram for the industry and a separate diagram for the individual taxi company.)
(ii) To what extent does the monopolistic competition model accurately reflect the taxi market in Victoria?
(iii) To what extent does the oligopoly, or the monopoly, model accurately reflect the taxi market in Victoria?
c) The Victorian taxi industry is regulated by the Taxi Services Commission (TSC). The TSC issues taxi licences, accredits drivers, and ensures that the industry complies with legislation and regulations (http://taxi.vic.gov.au/about-us/taxiservices-commission).
(i) Use demand and supply analysis to illustrate and assess the impact of licences on the supply of taxi rides and the price of taxi rides, in the scenario where the TSC does not limit the absolute number of taxis but merely sets a licence fee for all taxis. For this question ignore all the other activities of the TSC and assume that they only regulate tax licences.
(ii) Use demand and supply analysis to illustrate and assess the impact of licences on the supply of taxi rides and the price of taxi rides, in the scenario where the TSC sets a limit on the absolute number of taxis and sets a licence fee for all taxis. For this question ignore all the other activities of the TSC and assume that they only regulate tax licences.
(iii) The TSC also sets the maximum fares that taxis can charge. Use demand the price of a taxi ride and the number of taxi rides in Victoria. For this and supply analysis to illustrate and assess the impact of fare regulation on question ignore all the other activities of the TSC and assume that they only regulate taxi fares.
(iv) In contrast to taxis, UberX is currently not regulated in Victoria; UberX faces neither licence nor fare regulation. What impact does this difference in regulation have on competition in the taxi and ride-sharing industry?
(v) Fare regulation is often supported by politicians because of the view that there is a corporate social responsibility to make taxi travel affordable. What other options are there to support those who would otherwise find taxi travel too costly?
Task 2: Prices
(i) Construct a time series graph of the price of a Victorian license, for the years 2004 to 2014 (plot the years on the horizontal axis and the price of the licence on the vertical axis). The data can be collected from the Australian Taxi Industry Association webpage: http://www.atia.com.au/taxi-statistics/. You can use Excel or any other program to construct the graph.
(ii) Referring to the graph you constructed in (i) above, discuss the patterns in the value of the taxi license.
(iii) It is often claimed that the introduction of Uber in 2012 led to a collapse in the taxi license price. Evaluate this claim with reference to the time series graph you constructed in part (i)? What factors other than Uber affect the taxi license price?
b) According to the Taxi Services Commission webpage: “In metropolitan Melbourne, you will pay the lowest fares during the day, a little more for overnight and peak fares after 10pm on Friday and Saturday nights.” Explain the logic behind the regulator changing the fixed price for taxi services so that it varies over the course of the day and across the week.
c) One feature of Uber is ‘surge pricing’. This makes Uber prices less predictable. Use a diagram to illustrate and explain the economics behind surge pricing. You may find the following useful background reading:
Part 2: Economics of Military Conflict
a) Dube and Vargas (2013) argue that the value of coffee production, i.e. the price of coffee times the area of land under coffee cultivation is an important determinant of conflict in Colombia. Using the data on Colombian armed conflict, construct a scatter diagram that shows the relationship between the number of attacks (on the horizontal axis) and the value of coffee production (on the vertical axis). The data can be found in the Assessment Resources folder as the Excel file Conflict in Colombia. You can use Excel or any other software to construct a scatter diagram.
(i) What does the scatter diagram tell us about the relationship between the number of guerrilla attacks and the value of coffee production? (ii) Explain how the concept of opportunity cost might explain this relationship.
b) Similar to a) above, construct a graph that shows the relationship between number of casualties (on the horizontal axis) and value of coffee production (on the vertical axis). What does the graph tell us about the relationship between the number of casualties and the value of coffee production?
c) In this question we consider policy options to reduce violent conflict.
(i) Do the results from a) and b) above suggest that the Colombian government should stabilize the price of coffee? What are the costs of price stabilization?
(ii) The Colombian government and the main rebel group have recently agreed to a bilateral ceasefire. This includes two economic dimensions: land reform involving redistribution of land to poor farmers, and the end of illegal drug trade, with drug production to be replaced by alternate crops. Explain how these ceasefire conditions relate to opportunity cost. How successful do you think drug trade elimination will be if the world price of illegal drugs increases?
Solution.
Disruptive Technologies- UberX
Part A: Disruptive Technologies
- Based on a trial to establish the cheaper means of transport between the UberX and other Taxi service providers across Sydney, it was established the UberX taxis were more inexpensive compared to Standard taxis. 56 rides (i.e. 28 rides using the UberX and 28 using standard taxis) using the same route were conducted for the trial. The UberX taxis were found to be cheaper 9 out of 10 times compared to the standard taxis. In other words. UberX was 40% less expensive than the standards taxis. The comparison was clearer considering the cost of a one-kilometre drive using UberX and Standard Taxi. For example, it costs $1.45 to travel a distance of One Kilometre using UberX while it would cost $2.19 to cover the same distance using the Standard taxis. Therefore, it would be cheaper to ride using an UberX taxi from Deakin University, Burwood campus to the Melbourne Tullamarine airport than riding using a Standard Taxi.
- In the monopolistic competition type of the industry, there are many consumers and many consumers while the products are slightly differentiated. Although the producers are the price makers, the consumers have the power to switch from one provider to another. This is a perfect explanation of the Australian Taxi Industry before and after the entry of the UberX taxi service.
In the Short run (i.e. before the entry of UberX, the Standard (Private) taxis used to make abnormal profits as illustrated in the graph below;
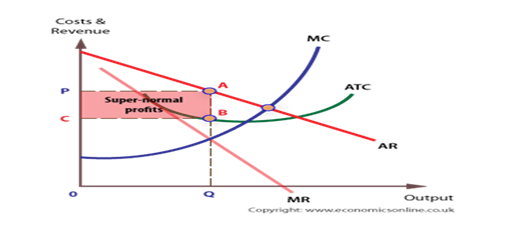
With less product differentiation, consumers in the Australian taxi industry have no influence over the prices of the services provided to them. Therefore the Taxi owners are the price makers. Second, the industry is unregulated therefore, the producers can agree upon themselves to hike their prices leading to supernormal profit shown in the graph above.
UberX‘s monopolistic graph in the Long run
In the short run, businesses operating in a monopolistic industry make abnormal profits which are likely to attract new entrants in the market. Unlike the monopoly industry where new entrant is limited, monopolistic industry has no barrier for new entrants.
Therefore, new entrants means new competition, emergence of price wars, and reduction of the prices. As new entrants are made, consumers tend to prefer the services provided by the new firms. Therefore, the demand curve for the existing companies shift to the left. With time the profit-maximising level is achieved because the MR=MC. At this point, the firms operating in a monopolistic industry will earn normal prices as opposed to supernormal ones. The Monopolistic competition graph in the long run can be represented as shown below.
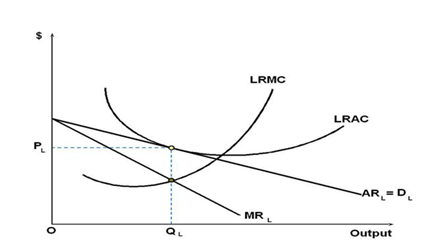
Just like in other cities, the operations in the Australian Taxi industry was disrupted after the entry of Uber-Company. One advantage that Uber enjoys is that it provides cheaper services as compared to the traditional taxis. Its Smartphone based cab services have been an integral part for its market entrant as well as gaining trust and favor among the consumers. The changes in the Australian Taxi Industry before and after the entry of UberX Company is summarized graphically as shown below.
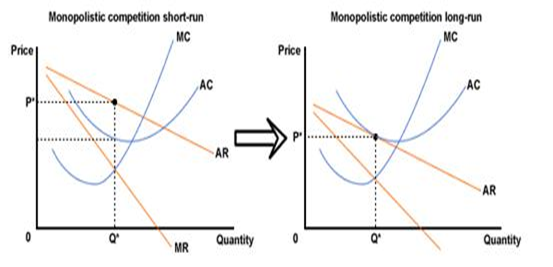
- To what extent does the monopolistic competition model accurately reflect the taxi market in Victoria?
The Victorian taxi market is a perfect definition of monopolistic competition. The tradition taxis were earning supernormal profits which attracted new entrants such as the Uber taxi company in the Long run. Second, there is no entrant barrier which can be seen from the Uber’s entrants in the market; this is a descriptive factor for a monopolistic market. From the illustrations above, the demand for services provided by old players shifts to the left as new firms entered the market. In the long run, the economic profits would not be earned by the firms because the marginal revenue is equal to the marginal cost. Therefore, with the increase of competition from the Uber-Company, firms in the Victoria Taxi market can only make normal profits.
- To what extent does the oligopoly, or the monopoly, model accurately reflect the taxi market in Victoria?
The Victorian market can be defined as an Oligopoly to some extent. Oligopoly market is defined as a where competition is limited competition because there is a small number of producers or service providers in the market. In the Victorian taxi, market is dominated by two main rivals, that is, the traditional taxi cabs and the Uber taxis. Just like under monopolistic markets, producers in the oligopoly market are price makers while consumers are price takers. However, every producer determines the price for its products or services. In the Victoria market, both Uber and traditional taxi cabs determine their services.
C)
- The factors of demand and supply have a major impact on the price at which products and services are provided in the market as well as on the quantity supplied in the market. When the market is unregulated, there are many taxi service providers in the Victorian market. However, when the Taxi Service Commission (TSC), sets the minimum license fee for all taxis, the number of service providers is likely to reduce. The reduction in the number of taxi service providers would arise because some cab owners would not meet the license fee demanded by the TSC.
Therefore, the supply of taxi services would decrease hence the price charged for the taxi services would increase. Where license fee is a major determinant factor (other factors remaining constant), the demand by the customers would increase because of the reduced quantity supplied by the providers. Under this scenario, the supply curve would shifts to the left prompting the price of the taxi services to increase as summarized in the demand-supply curve below.
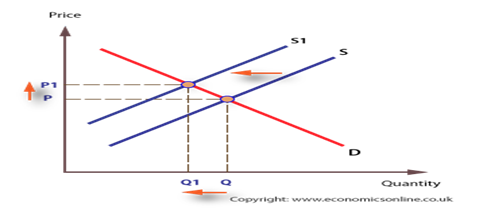
- If the TSC sets a limit on the absolute number of taxis to operate in the Victoria market and sets a license fee for all taxis, then two scenarios would arise. The license fee would affect all the taxis, and hence there would be no significant changes in the market: only those who cannot meet the fee would be affected. If the number of the taxis operating in the market is set below the current number, then the quantity supplied by the providers would reduce and hence the price for taxi services would increase. If the number of taxis operating in Victoria is set above the current number, then new entrants will find their way on the market. Therefore, the quantity supplied would increase hence reducing the price of taxi services.
TSC is more likely to regulate the taxi prices to favour the consumers rather than favouring the services providers. However, the set fare should be reasonable enough for the industry growth. Nevertheless, the producers would not enjoy the price making strategy. Some suppliers are likely to leave the industry citing low level of profitability. Therefore, with a reduced fare prices, the demand for taxi services among the consumers would increase because the services would be deemed as affordable.
- Where other traditional taxis are regulated regarding licensing and fare while the UberX is not. The latter would practice price discrimination to maximize its profit. For example, UberX might choose to increase its fare prices when the demand is high and reduce the prices when the demand is low. This is an advantage that the tradition taxis would not have.
- Apart from fare price regulation to promote corporate social responsibility, Taxi services providers such of Uber can support social activities such as engaging in campaigns that promote healthy eating to reduce obesity among the youths, sponsor sport and educational activities. Likewise, they can engage in environmentally friendly practices as well as provide bonuses and discounts to their customers.
Task 2: Prices
- Construct a time series graph of the price of a Victorian license, for the years 2004 to 2014
Ti
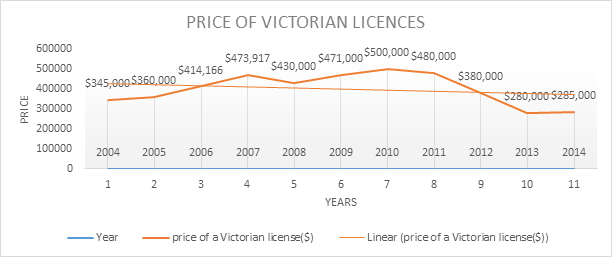
II. Discuss the patterns in the value of the taxi license
The price of the taxi licensing in Victoria was highest in 2010 at $ 500,000 and lowest in 2013 at $280,000. Between 2004 and 2007, the price rose before slightly falling in 2008. Between 2009 and 2010, the price rose again before falling from 2011 to 2014. Based on the trend line (linear), the Victorian price of licensing the taxi have been decreasing gradually.
III. The time series above shows that the license prices in Victoria had reduced between 2012 and 2014. This trend is in support of the statement that the reduction was prompted by the introduction of the UberX taxi services in the market.
Apart from the entry of UberX, the TSC, a representative of the government, may have reduced the licencing price to promote self-employment among the Victorian residents. Likewise, UberX being a foreign company, the TSC might have deemed it effective to reduce the price and promote local companies and make them competitive enough against UberX. Lastly, the move might have been meant to enhance economic growth.
- Using the different price for the taxi services, TSC directly applied the concept of demand and supply. During the day when few residents commute to and from their workplaces, the prices are lower to attract more consumers. With high demand for the taxi services, TSC lowered the prices to protect the consumers against exploitation from the service providers and attract more consumers. In the evenings and Overnight, most people return to their homes from work. The TSC might have increased the prices to take advantage of the high demand for taxi services. The same case applies the Friday and Saturday nights when the price is at the peak.
- Uber’s surge pricing
Surge pricing refers to increasing the price of a product of service when its demand is high. Uber is well known for surge pricing to provide services to the available and reliable consumers who are willing to pay more. Uber’s strategy for surge pricing is shown below;
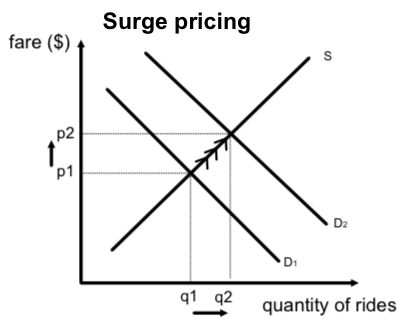
Surge pricing occurs when the demand for Uber taxi services shift from D1 to D2 prompting the price (fare) to increase from P1 to P2.
PART 2
a)

