Workflow Analysis Sample Paper
Creating a Flowchart (OR your title)
Your Name
Walden University
Course number and section
Instructor’s name
Date
Creating a Flowchart
Type your introduction here.
E.g. According to McGonigle and Mastrian (2012), “Observation and documentation of workflow to understand better what is happening in the current environment and how it can be altered is referred to as ‘process’ or ‘workflow analysis” (p. 266).
Tell us about the process you are going to use in your diagram. (Research and cite)
Stakeholders (Who does this help?)
When forming a workflow analysis team, it is important to include participants who are able to contribute information regarding current workflow and are willing to suggest ideas for future state improvement (McGonigle & Mastrian, 2012). As indicated in the attached flowchart, the stakeholders participating in the workflow… (Research and cite)
The Current Process
Here is the section where you explain in words what your diagram shows. Needless to say, it should correlate.
Technology Used
The technology that is used for this workflow is… (Research and cite)
Policies and Rules
The policies and rules in place to assist with this workflow diagrams are… (Research and cite)
Metrics Used to Measure Workflow Performance
McGonigle & Mastrian (2012) defined metrics as a measure of accomplishment of the “right workflow complement” (p. 276). Data is necessary to determine how a process is performing. In your opinion, is the metric effective? Why so? (Research and cite)
Areas for Improvement
The current workflow in my organization that is outlined in this diagram could be improved. There needs to be… (Research and cite)
Summary OR Conclusion (your choice but only one of the two)
Summarize and conclude here.
References
(These references are samples only)
Laureate Education, Inc. (Executive Producer). (2012c). Health care technologies. Baltimore, MD: Author.
McGonigle, D., & Mastrian, K. G. (2012). Nursing informatics and the foundation of knowledge (2nd ed.). Burlington, MA: Jones and Bartlett Learning.
U.S. Department of Health & Human
Services (n.d.). Workflow assessment for health IT toolkit.
Retrieved from http://healthit.ahrq.gov/health-it-tools-and-resources.
IMPORTANT
- Read and understand ALL the instructions before starting your paper.
- Meet ALL the requirements.
- Avoid websites such as Wikipedia, Answers.com, etc… Instead, use your course material, and if more references are required, browse the University library to find quality journal articles.
- Remember: 4-5 pages + title page + RL.
Note: This paper will serve as the Portfolio Assignment for the course. So, pay special attention. After your paper is graded, you may want to go back and fix what needs to be fixed so it will look good in your portfolio.
Creating a Flowchart Workflow analysis aims to determine workflow patterns that maximize the effective use of resources and minimize activities that do not add value. There are a variety of tools that can be used to analyze the workflow of processes and clarify potential avenues for eliminating waste. Flowcharts are a basic and commonly used workflow analysis method that can help highlight areas in need of streamlining. In this Assignment, you select a common event that occurs regularly in your organization and create a flowchart representing the workflow. You analyze the process you have diagrammed and propose changes for improvement.
To prepare:
Identify a common, simple event that frequently occurs in your organization that you would like to evaluate.
Consider how you would design a flowchart to represent the current workflow.
Consider what metrics you would use to determine the effectiveness of the current workflow and identify areas of waste.
To complete:
Write a 3- to 5-page paper which includes the following:
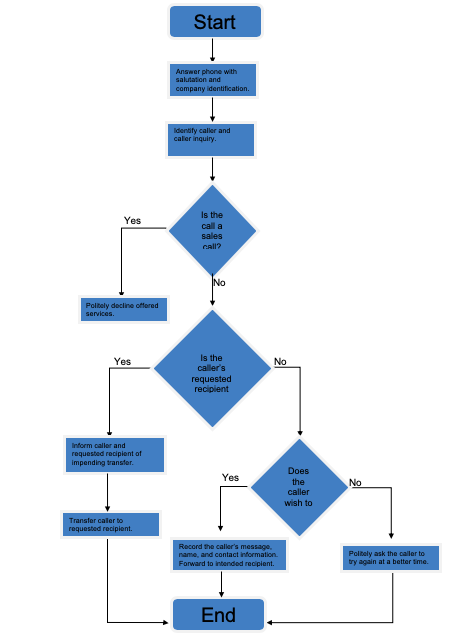
Create a simple flowchart of the activity you selected. (Review the Sample Workflow of Answering a Telephone in an Office document found in this week’s Learning Resources for an example.)
Next, in your paper: Explain the process you have diagrammed.
For each step or decision point in the process, identify the following: Who does this step? (It can be several people.)
What technology is used?
What policies and rules are involved in determining how, when, why, or where the step is executed?
What information is needed for the execution of this step?
Describe the metric that is currently used to measure the soundness of the workflow. Is it effective?
Describe any areas where improvements could occur and propose changes that could bring about these improvements in the workflow.
Summarize why it is important to be aware of the flow of an activity.
Remember to include a cover page, introduction, and summary for your paper. This Assignment is due by Day 7 of Week 8. Note: This paper will serve as the Portfolio Assignment for the course.
Solution
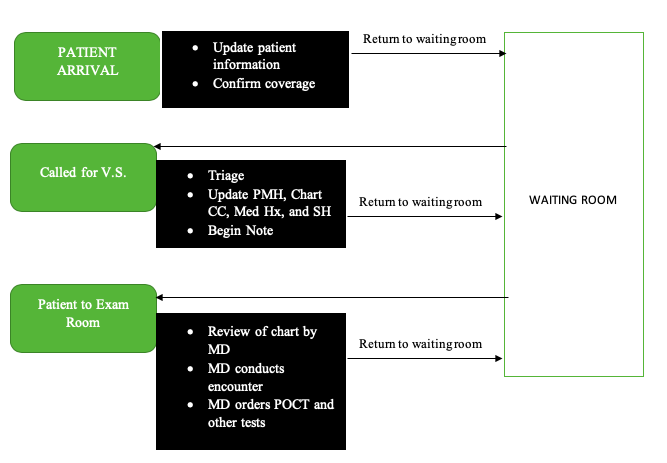
Patient Intake Workflow Analysis
Workflow analysis is an integral part of a holistic approach to establishing usable information systems. According to Whittenburg (2010), workflow analysis is the review of any process that takes place within the healthcare setting in order to determine its future state, areas that require improvement and improvements that would be most effective. As such, workflow is any process within the healthcare system and it is not linear, but rather it is dynamic and moves between various organizational levels. Workflow analysis involves the use of specific tools to analyze workflow to allow for proper IT planning, continuous improvement, and implementation (Whittenburg, 2010). This paper is going to use the workflow flow chart attached to analyze the initial steps taken by a patient during a visit at our organization in order to determine areas that can be improved on using IT approaches, especially EHR.
Stakeholders
The process of workflow analysis requires the participation of the various stakeholders engaged in the workflow as they form the best sources of information concerning the current state of the process and their experience with the process (Avni, 2007). The initial steps taken by a patient during a visit at the hospital mainly involve the nurse and the Medical Doctor (MD) as the stakeholders. It is the nurse who ushers in the patient and obtains the initial vital information from the patient before forwarding the information and the patient to the medical Doctor for further review.
The Current Process
The current process involving the initial steps of the patient during encounter on paper has been show on the flow chart. The first step involves patient arrival, in which information is updated by the nurse and coverage is confirmed. The patient then returns to waiting. Then the patient is called for V.S. and the triage nurse will assess the patient’s condition and any changes that have occurred in order to determine the priority for treatment or Emergency Room admission. The nurse then begins the patient’s note with results of the initial assessment. The nurse also charts the chief complaint, updates the patient’s past medical history, medical history, and social history. The patient again returns to waiting. The last step of this initial process involves the nurse directing the patient to the examination room. The MD reviews the chart outside the room and then conducts a clinical encounter, which involves interviewing the patient further to obtain signs and symptoms and any other historical factors that could prompt a diagnosis. The MD then orders for Point-Of-Care-Testing (POCT) and any other tests in order to determine a complete diagnosis of the patient, according to the provided information. The patient again returns to waiting.
Technology Used
This workflow only involves a computer as the only technology used at to document the patient information during the initial stage of the process and to check for coverage. The rest of the steps still rely on the traditional approaches that involve documentation on paper and the nurse physically taking the chart with patient information to the MD and placing it outside their office. The computer has been increasingly integrated into the hospital setting as a major technology in storing and referring to patient information during successive visits. It is highly reliable especially when it comes to accessing the patient’s initial information as opposed to the traditional method, which involved going through paper files in order to get such information (Unertl, Johnson, & Lorenzi, 2012).
Policies and Rules
This workflow will employ Policy No. 9420, which includes the “maintenance of the medical records” standards. Under this policy, it is required that medical records of every individual that is treated or evaluated as an outpatient, inpatient, or emergency patient to have their medical record maintained (University of California, 2013). The policy also provides that medical records should be maintained as electronic or hardcopy (paper) formats, inclusive of digital images, films, and photographs, among others. In addition, the policy requires Original Medical record documents to be sent to department of Medical Records, including the chart with original reports (University of California, 2013).
Metrics Used to Measure Workflow Performance
Quantitative or qualitative information is important in determining the performance of workflow. As such, quality improvement is integral in any patient-centered health-care efforts, with there being the need for employment of relevant performance measures that will ensure that care is comprehensively improved (Kansagara, et al., 2014). In the case of the initial steps of the patient during visit on paper, the main metric used to measure workflow performance is the time taken for the patient to be served to completion where he or she is either leaves the hospital or admitted to inpatient. Another metric is the proper sharing of information about the patient between the nurse and the medical doctor.
Areas of Improvement
The current process is less effective as it involves multiple returns of the patient to the waiting room. As such, it takes the patient longer to be completely served as they have to wait for information to be shared between the clinicians, which is a slow process as there is minimal use of technology. Such inefficient application of information technology could also be considered a contributory factor to other issues that hamper the quality of care provided. Such issues include inconsistent support of the nurses from the clinician, failure of the nurses to meet the individual expectations of the MDs, nurses trying to guess the needs of the MDs, and disorganized practice, which inconveniences the patient. The major areas that require improvement include the process of patient intake that takes too long, the burdensome process of medicine refills, and the inconsistent availability of results from the laboratory. This can be improved through application of electronic medical records. This would allow for updating of patient information using the Practice Management System during patient intake. An encounter note would then be generated by the EPM (Kumar & Aldrich, 2010). The patient will then be taken to an empty Examination Room with a computer, in which the nurse would take V.S., PMH, C.C., and Med History. The MD would then visit the patient in the Exam room and use the system to order POCT and any other tests. The patient would then remain in the room and the Flag would notify the nurse of the MD’s order (Kumar & Aldrich, 2010). The visit would then be finalized. This process would reduce the number of returns patients make to the waiting room from three to zero.
Conclusion
It is evident that the current process of patient intake and encounter in the hospital is slow and highly inconveniencing for the patient. As such, IT would allow for proper sharing of information between the clinicians and thus promote quicker availability of information on the patient and hence care for the patient. The Electronic medical records system would allow for proper sharing of such information and reduction of patient returns to the waiting room by providing for a way in which the required information is quickly availed through the system and the burdensome writing of notes and reports is taken up by the computer.
References
Avni, T. (2007). Value stream mapping and simulation modeling: an integrated approach to workflow analysis in healthcare. Journal for Healthcare Quality: Promoting Excellence in Healthcare, 29(5), W5-3.
Kansagara, D., Tuepker, A., Joos, S., Nicolaidis, C., Skaperdas, E., & Hickam, D. (2014). Getting Performance Metrics Right: A Qualitative Study of Staff Experiences Implementing and Measuring Practice Transformation. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 29(2), 607-613.
Kumar, S., & Aldrich, K. (2010). Overcoming barriers to electronic medical record (EMR) implementation in the US healthcare system: A comparative study. Health Informatics Journal, 16(4), 306-318.
Unertl, K. M., Johnson, K. B., & Lorenzi, N. M. (2012). Health information exchange technology on the front lines of healthcare: workflow factors and patterns of use. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 19(3), 392-400.
University of California. (2013). Legal Medical Records Standards. Retrieved from University of California: http://policy.ucop.edu/doc/1100168/LegalMedicalRecord
Whittenburg, L. (2010). Workflow viewpoints: Analysis of nursing workflow documentation in the electronic health record. Journal Of Healthcare Information Management, 24(3), 71-75.