Comparison of Two Types of Operational Budgets paper
Paper details:
In preparation for this assignment, you may find it helpful to refer to Finkler, S. A., Koyner, C.T., & Jones, C.B. (2012). Financial management for nurse managers and executives (4th ed.). St. Louis, MO: Elsevier. Chapter 12.
This assignment asks you to look at two budget methodologies. You are asked to focus your discussion on two types of operational budgets and then compare them to the identified criteria. Lastly, you are asked to present an example of how one budget type would be used by the masters prepared nurse leader in a health care setting of your choice.
Follow these instructions for writing your Comparison of Two Types of Operational Budgets paper. Keep the paper within a 6 page limit (excluding title page and reference list). An abstract page is not required for this assignment.
Budget Types/Methodologies (20%)
A. Compare the fixed operating budget approach to the flexible operating budget approach as outlined in your text book readings. Finkler, S. A., Koyner, C.T., & Jones, C.B. (2012). Financial management for nurse managers and executives (4th ed.). St. Louis, MO: Elsevier.
B. Describe these two budget methodologies.
C. Include enough detail for the reader to follow and understand the methodology.
Chart
Construct a chart and compare your chosen budget methodology in the following categories: 40%
A. Advantages/disadvantages to the nurse leader in monitoring compliance
B. Operations best suited to each type of budget
C. Impact on the correlation to patient care
D. Ability to take variances into account
Example of Budget (20%)
Choose one of the budget types you have described.
A. Present an example of how this budget type would be used by the masters prepared nurse leader in a health care setting of your choice.
B. The setting can be a community or inpatient environment where you work, have worked, or would like to work as a masters prepared nurse leader.
Integration of Evidence and Theory 10%
Integrate credible, relevant sources to support ideas appropriate for the assignment.
Consistently use information in ways that are true to original context. Always distinguish between own ideas or common knowledge and ideas requiring attribution.
Scholarly articles integrated within the paper meet the following standards:
Provide the required number of references (minimum of 6)
Most nursing-specific or nursing-related
Provide the required number of references from a discipline outside nursing (minimum of 1).
Published within 5 years OR published beyond 5 years if seminal source or gap in the literature
5. Organization, writing style, grammar, usage, mechanics, formatting, and length 10%
Follow APA Guidelines for the title page, abstract, headings and subheadings, citations, and references.
The presentation and style of the paper are consistent with
scholarly work and reflect use of APA format (6th ed.)
Page Limit: 6 pages
Use clear structure as outlined in the assignment with all components present, including brief and succinct abstract, introduction, and conclusion.
Use straightforward, clear, concise, nearly error-free language that conveys meaning to readers.
Conform to APA formatting standards, with only minor deviations.
Solution
Types of Operational Budgets in Healthcare
Introduction
The process of creating efficient operational budgets is critical for the promotion of efficiency and the quality of care in any healthcare organization. It creates a plan for the revenues and the expenses of the next year and such different organizational units, departments and the management and leadership must work closely to identify and utilize the most efficient budgeting approach. The major issue for consideration before the preparation of the revenue and expense portions of the operating budget is volume forecasting. What follows is the estimation of revenues and expenses using evidence from past records obtained through an in-depth analysis. The creation of a patient-volume forecast makes it possible for the management to determine the revenue, the appropriate staffing, clinical needs, supplies and other expenses. Most importantly, it is important to consider concerns such as time management, attitude towards the budget process and accuracy. This essay compares different operational budgets and applies the case of the XYZ Healthcare Organization to outline the importance and effectiveness of the approaches.
Fixed and Flexible Operational Budgets
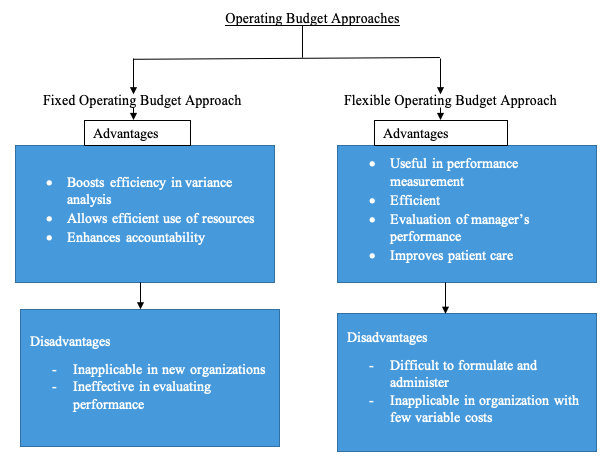
According to Penner (2004), the operating budget approach is an itemized outline of the revenue and the expenses a program, department, or an organization generates over a specific period in relation to or in the provision of goods and services. In the healthcare setting, the expenses and revenue are accrued from the provision of health care services. The two major operating budget approaches are the fixed and the flexible operating budget methodologies. The comparison of these methodologies in their formats and application depict the differences and the effectiveness or lack of it in the integration in healthcare organizations. Finkler and Ward (2005) state that the major difference between the two approaches is that the fixed budget approach itemizes expenses or revenues for fixed volume of service units while the flexible budget approach adjusts the operating expenses in accordance with the variation in volume. The fixed budget remains the same throughout a fiscal year regardless of the volume while the flexible budgeting approach changes the costs for the provision of services in line with the changes in volume. The volume variation in the flexible approach also changes the revenues.
The fixed operating budget approach is frequently applied in the health care setting in the itemization of expenses for an unchanging volume of service units. The approach is applied with the integration of extensive analysis of the past and the application of the information to forecast the future. The budget approach involves planning done ahead of time, sometimes as early as a year before the specified time. According to (Finkler & Ward, 2005), the plans are further broken down into smaller and distinct reporting periods. For instance, the application of the approach in the XYZ organization would require planning and the development of a budget that follows the forecasted revenues and expenses to create a budget that spans for two years. The budget might then be divided into semi-annual or quarterly reporting periods to ensure efficiency and effective implementation of the plan. The consideration of variance analysis and integration in organizational management through the application of the fixed budgeting approach allows the organization to promote efficiency in budgeting to minimize misuse, underuse, and overuse. As such, the approach is suitable for businesses that have existed for several years as new businesses lack the data records and information for forecasting and developing the budget.
The flexible budget involves the calculation of various expenses for variable costs that cause a change in the actual revenue. The budget that utilizes this approach varies depending on the changes experienced on the expenditure levels. Before the development of the flexible operating budget, the management and the different units and departments must consider and follow certain procedures. It is important to identify the fixed costs and determine the extent to which the variable costs are likely to change as the organization records changes in volume. The method is sophisticated in comparison with the fixed approach and offers room for adjusting the budget in accordance with the budgeting objectives. The changes in revenue, causes a change in the expenses, and thus, it is important to understand how the changing revenue affects the expenses. The approach provides a significant level of control and enhances the level of efficiency by offering effective forecasting (Finkler, Kovner, & Jones, 2007). The method is suitable for new businesses that must always put the costs under constant review, analysis and control.
The operating budget approaches have advantages and disadvantages that must be considered before application in any organization. For instance, the flexible operating budget is useful in performance measurement, useful in businesses where the costs are closely aligned with activity levels, and is a more efficient budgeting approach. Its efficiency allows for easier and fast updating of the budget in cases where the finalization of the revenue or volume figures is due. Moreover, it restructures itself depending on the changes and, therefore, can be applied in the evaluation of managers’ performance (Finkler, Kovner, & Jones, 2007). On the other hand, the fixed operating budget minimizes overuse, misuse and underuse of organizational resources. As such, its application ensures accountability and the efficient use of resources. Moreover, the flexible approach is difficult to formulate and administer and reveals impossibility in comparison of the actual revenue to the budgeted revenue since the values are the same. Additionally, organizations with few variable costs may find the fixed operating budget approach inapplicable. While this is the case, the fixed approach is ineffective for the evaluation of performance and is inapplicable in new organizations (Penner, 2004).
Operating Budget Approaches
Fixed Operating Budget Approach Flexible Operating Budget Approach
XYZ Hospital Flexible Operating Budget (FOB) for 2016/2017
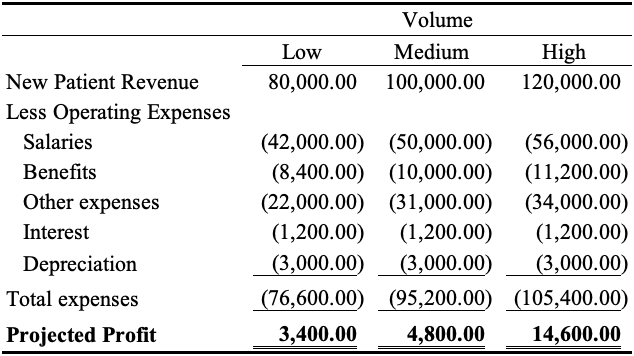
The budget assumes a fixed salary of $22 000 and experienced minimal to no significant change with relatively small changes in volume. The drop in the salaries in the lower and the higher volume cases represents a directly proportional change for the percentage of the salary costs that are variable. Additionally, the other expenses which include items such as supplies in the XYZ organization were taken as variables. While this is the case, the organization will record changes in benefits in the proportion of the salary changes. Moreover, a fall in the volume will prompt a fall in the profit efficiency of the organization while an increase in volume triggers a significant rise in the profitability of the organization. All notwithstanding, the organization must create and implement a contingency plan that will consistently respond to the drop in volume to ensure a decrease in the number of staff. This plan will ensure that the revenue of the XYZ decreases or increase in the proportion of volume changes. The integration of this budget will play a critical role in the enhancement of efficiency. Cases of volume declines must be followed by aggressive adjustment of volume costs downwards to ensure efficiency but without compromising the quality of care.
Conclusion
Efficient budgeting is critical for
enhanced efficiency in healthcare organizations. The operating budget helps in
planning the expenses and revenues of the future fiscal years or years in a
healthcare organization. It itemizes the revenues and expenses of an
organization after the consideration of different factors and the analysis of
past records to predict the future. The fixed and flexible operating budget
approaches are key budgeting approaches frequently applied in healthcare
settings. The former itemizes expenses and revenues for fixed volume of service
units without variations throughout the fiscal year while the latter adjusts
the operating expenses in accordance with the variation in volume, and thus
revenues change accordingly. Healthcare organizations apply the different approaches
after the consideration of the effectiveness of each depending on the present
circumstances. The application of the flexible operating budget in the XYZ
Healthcare Organization will enhance efficiency in the delivery of care and the
management of organizational resources.
References
Finkler, S. A., & Ward, D. M. (2005). Cost accounting for health care organizations: concepts and applications. Gaithersburg: Aspen Publishers.
Finkler, S. A., Kovner, C. T., & Jones, C. B. (2007). Financial management for nurse managers and executives. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier.
Penner, S. J. (2004). Introduction to health care economics & financial management: fundamental concepts with practical applications. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.

