Evidence-based practice & applied nursing research
Topic Selected: Nursing medication errors
Solution
Evidence-Based Practice & Applied Nursing Research: Medication Errors
Section A
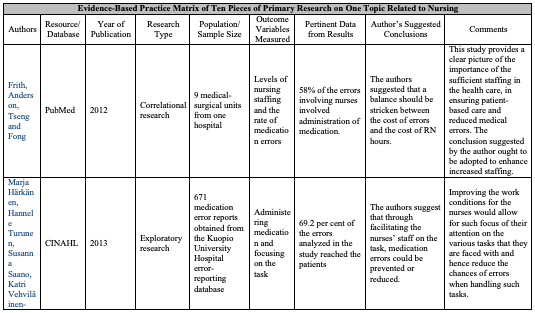
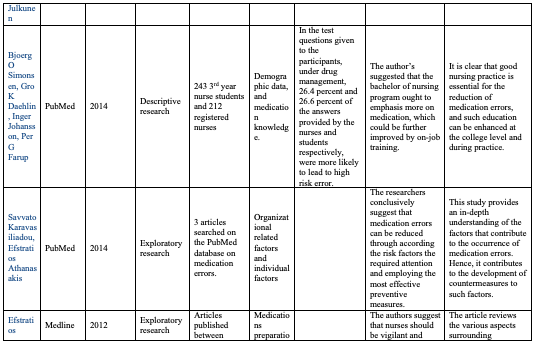
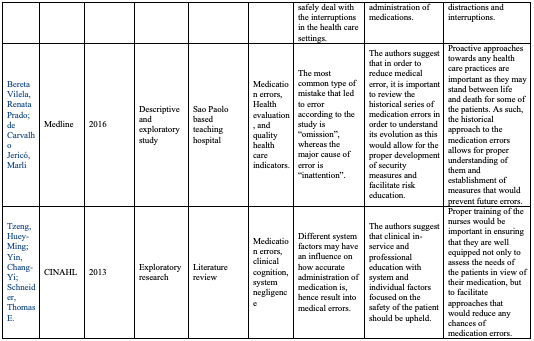
Frith, K. H., Anderson, E. F., Tseng, F., & Fong, E. A. (2012). Nurse Staffing Is an Important Strategy to Prevent Medication Errors in Community Hospitals. Nursing Economics, 30(5), 288-294.
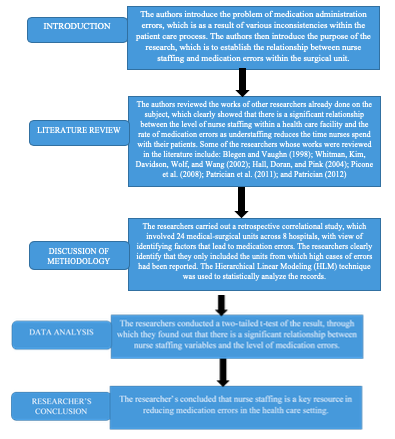
There is a strong link between the evidence provided in the research and the conclusions upheld by the researchers. Reductions in nurse staffing across the medical-surgical units showed an increase in the number of medication errors reported. On the other hand, for the medical surgical units that did not have staffing problems, less medication errors were reported. The link between nurse staffing and medication errors is thus clear, with various implications for nurses existing including the high costs of medication errors in terms of litigations, long periods of patient stays at the health care organization, and compensation costs, among others. As much as the costs of such medication errors for nurses have not been quantified in the research, they cannot be ignored.
One
of the major ethical concerns that the researchers likely experienced during
the research involves upholding the privacy of patient data. Health care
organizations are not expected to disclose patient data to third parties, and
hence if the researchers received consent to interact with patient data in view
of combining their data on the kind of medication errors that had been
experienced across the units, they were highly expected to uphold
confidentiality. The researcher approached the research retrospectively, basing
their findings on recorded data in terms of errors and staffing figures within
the units. This is the best approach for the study as it provides quantifiable
data that can be statistically analyzed to offer an insight into the findings.
Nevertheless, the researchers could also have performed a survey among the nurses
by administering questionnaires in order to establish their perception
concerning the impact of staffing on medication errors. This would also offer
primary data concerning the association between staffing and medication errors.
Section B

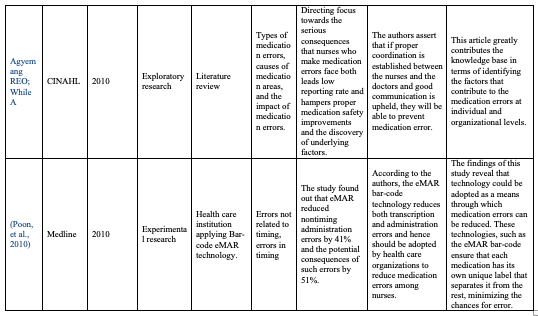
References
Agyemang, R., & While, A. (2010). Medication errors: types, causes and impact on nursing practice. British Journal of Nursing, 19(6), 380-385.
Athanasakis, E. (2012). Prevention of medication errors made by nurses in clinical practice. Health Science Journal, 6(4), 773-783.
Frith, K. H., Anderson, E. F., Tseng, F., & Fong, E. A. (2012). Nurse Staffing Is an Important Strategy to Prevent Medication Errors in Community Hospitals. Nursing Economics, 30(5), 288-294.
Härkänen, M., Turunen, H., Saano, S., & Vehviläinen-Julkunen, K. (2013). Medication errors: what hospital reports reveal about staff views. Nursing Education, 19(10), 32-37.
Hayes, C., Jackson, D., Davidson, P. M., & Power, T. (2015). Medication errors in hospitals: a literature review of disruptions to nursing practice during medication administration. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 24(21/22), 3063-3076.
Karavasiliadou, S., & Athanasakis, E. (2014). An inside look into the factors contributing to medication errors in the clinical nursing practice. Health Science Journal, 8(1), 32-44.
Poon, E. G., Keohane, C. A., Yoon, C. S., Ditmore, M., Bane, A., & Levtzion-Korach, O. (2010). Effect of Bar-Code Technology on the Safety. The New England Journal of Medicine, 362(18), 1698-1707.
Simonsen, B. O., Daehlin, G. K., Johansson, I., & Farup, P. G. (2014). Differences in medication knowledge and risk of errors between graduating nursing students and working registered nurses: comparative study. BMC Health Services Research, 14, 1-11.
Tzeng, H.-M., Yin, C.-Y., & Schneider, T. E. (2013). Medication Error-Related Issues In Nursing Practice. MEDSURG Nursing, 22(1), 13-50.
Vilela, R. P., & Jerico, M. d. (2016). Medication Errors: Management of the Medication Error Indicator Toward a More Safety Nursing Practice. Journal of Nursing, 10(1), 119-127.