Topic: Digital Business Innovation: Augmented Reality: what are the consequences for society?
- Demonstrate critical awareness of how digital business applications can support and change the way of doing business by aligning strategic and organisational goals
- Identify and evaluate digital business applications and their place in the internal value chain
- Critically appraise existing innovative technologies to fit operation requirements and meet strategic needs
- Identify and utilise appropriate methods for collecting, analysing and presenting data related to digital business.
- Demonstrate an ability to work effectively as an individual and group member in order to carry out tasks linking theory to practice so developing new skills to a high level
- Students will be able to review and diagnose knowledge (tacit and explicit) sharing in organisations to build critical thinking skills and digital literacy skill
- Communicate the solutions arrived at, and the theory underlying them, in verbal and written form to specialists and non-specialist audiences
- Locate, summarise and synthesise a range of information from published literature and electronic sources on digital business, innovative and disruptive technologies
Augmented Reality (AR) : what are the consequences for society Augmented Reality are becoming readily available and are defined as a live, direct or indirect, view of a physical, real-world environment whose elements are augmented by computer-generated sensory input such as sound, video, graphics or GPS data. Virtual reality replaces the real world with a simulated one. These technologies will have a significant impact on the way we live our lives. So what will be the consequences on the business landscape because of Augmented Reality? How will AR alter our societal practices of how we work and play? How will our perception alter of the already blurred real and virtual worlds? What different experiences could a business recreate and imagine with the concept of AR? How will people interact with both the digital and real? You are tasked with creating an academic poster supported by a short literature review and a reflective: 1. 40% of the module mark: Creating a well designed digital academic poster that includes:
a. Background of the Augmented Reality
b. Key positives that AR can bring to business
c. Key negatives that AR can bring to business
d. Make recommendations how society might harness the benefits or mitigate the negatives.
e. Best 3 posters get laminated 2. 50% of the module mark: A literature review to critically discuss the subject matter of your chosen topic area that will theoretically underpin the poster (1500 word limit with a 10%-/+)
a. You are asked to carry out a systematic search of The Library’s online databases, looking for peer-reviewed academic journal or conference papers. Your purpose is to discover relevant, peer-reviewed, academic research articles on your chosen topic area
b. Theoretical areas for discussion to choose from are: ethics and technology, privacy and surveillance of such technologies, AR and organisational change or AR and the cyborg.
c. Introduce your topic area and construct a balanced discussion this may include a comparison and contrast of different authors’ views on an issue, highlight areas in which authors are in disagreement, you can group authors who draw similar conclusions, offer a criticism on aspects of methodology, highlight exemplary studies and or gaps in research (50%) 3. 10% of the module mark: Reflection on learning and practice throughout the module. (300 word limit with a 10%-/+)
a. Focus on one area of learning or practice and use Gibbs Reflective Cycle to frame your discussion. Please add this to the end of your literature review
Solution
Augmented Reality
Introduction
Augmented Reality (AR) refers a view of a real physical world, either direct or indirect, whose images are supplemented (augmented) by a computer system of generating sensory inputs, including sound and video graphics as well as a GPS data (Geroimenko, 2014). It has been referred to as a mediated reality, in which the natural view of an object is supplemented or modified through computer techniques. The use of augmented reality involves the process of manipulating the virtual reality with an aim of duplicating the reality of the objects in the world in a computer. When using a system of augmented reality techniques, the user acquires a composite view of the image, which is a combination of the usual and natural look as initially perceived by the user, and the virtual scene that is a product of the augmented product. Considered as among the upcoming technologies, many business sectors have shown potential adoption of the technology, owing its ability to render desirable revolution in the way of doing things (Wassom & Bishop, 2015).
Possible impacts of digital business applications on the formulation of Business Strategies
Considering the fact different business ventures have unique operations, which require equally unique strategies, it is not easy to provide a definite answer as to the nature of the impact it may have on business strategy development (Pagani, 2013). various types of business ventures, including those dealing content creation, content owners, as well as publishers, service and product companies have unique systems of presenting their products to their customers, which have manifested a trend of migration from the initial analogue to digital business operations (Alem & Huang, 2011).
With the current trends of increased business transition from the analogue to digital platforms, it is possible to state that it would be a lot easier to find content, view and hear from the digital platforms over the web (Mithas, Tafti & Mitchell, 2013). For example, if there is a company that operates a current business as a content creation, such as building design, or if the firm manages a value addition service to the developed content, perhaps developing or publishing such content, there are chances that the company is undergoing the transition from analogue to digital, or completed such a process (Wassom & Bishop, 2015). Even though one can analyze the possible ways through which Augmented Reality can change the way people do business, it may be difficult to present an exhaustive list of such possible effects.
For product-based business, it is important to note that such products are often born out of demand and that modern process of product development depends on the nature of integrated technology (Wassom & Bishop, 2015). Each category of goods, ranging from food commodities to automobiles, has a type of digital data associated with them. Even though the integration and use of Augmented Reality continue to grow, there are chances that at its maturity, Augmented Reality would involve various man-made products. In this case, all types of products that have a physical presence and reality will have a similar or simulated digital presence, which would enhance the possible connection between uses.
Digital Business Applications and their Place in The Internal Value Chain
With the advancing technology, and the smooth spread of various technologies across the globe as a result of globalization, Digital Business Applications have led to a revolution in the manner in which business stakeholders operate. Business ventures such as Amazon, Netflix, Uber as well as Tesla have been leaders in the adoption of digital technologies in their value chain design (Barnes & Hunt, 2013). One of the most common strategies used in the approaches such companies have used is the disruption of their current marketing strategies, with an aim of dominating over their counterparts in the traditional business era.
In this case, such companies, alongside other digital based business ventures have taken a leading role in the use of technology-based strategies in formulating product design methods, manufacturing, sales, marketing as well as servicing (Pagani, 2013). In the modern era of doing business, it is most often possible to come across companies designing digital production systems, digital marketing sites, a mechanism of connected value chains, all which rely on Augmented Reality techniques as a way of making simulated realities of their products and services (Williams et.al, 2013).
In addition to the digitized systems of product manufacture, marketing, and sales, the digital business applications also reflect on the modern and dynamic on-demand type of servicing for customers. Companies and clients who have a digital presence have an easier way of interacting, particularly when customers have to choose and order for a product design from a list available from the online platforms. The new basket of modern technological business application technologies has rendered a revolution to change the traditional methods of doing business (Pagani, 2013).
APIs give various business ventures an opportunity to expose a particular contextual service as well as data for assigned customers. The significance of such data is to help the customers at the point of connection and interaction by making the process seamlessly easy for all types of business, including small venture apps such as kiosks, automobile app, or even a cloud app (Pagani, 2013). Furthermore, more opportunities for connecting, engaging as well as serving customers can also occur at the B2B companies such as Salesforce or Marketo, Uber or Amazon, in which there are a variety of apps through which their customers can use to transact business, regardless of time and place they are. The following is an example of a B2C digital value chain, which is the most shared and distinct in literature.
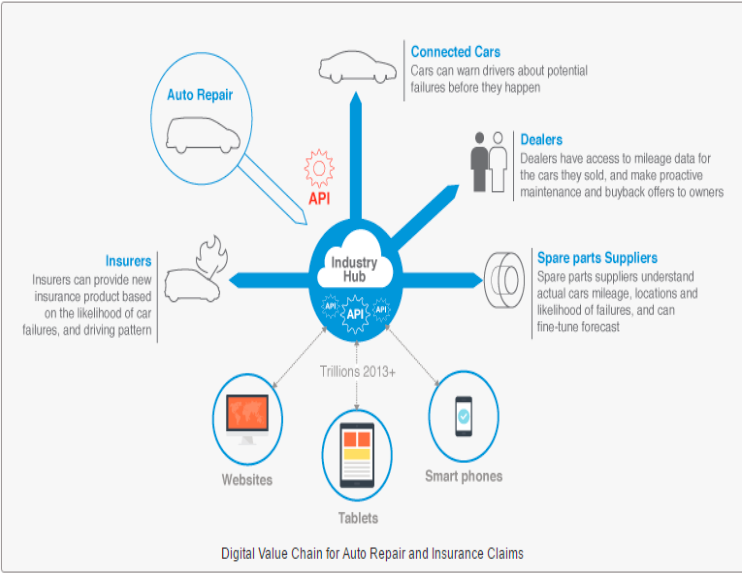
On the other hand, augmented reality and associated technologies have also been cited as among the leading factors that have enhanced social relationships across the globe. The thesis on the role of augmented reality, as modern technology, in improving social relationship has a basis on the increased levels of interconnectedness among people. It presents a comparison between the traditional days when human beings depended on limited means of communication to link up with their friends and peers (Pagani, 2013).
In this case, most people could only secure fewer friends and relatives within their localities. It was impossible and extremely expensive to find and keep in touch with various social relations. However, with increased levels of interconnectedness, through social media platforms, people can establish instant communication with their peers. People also take and share their pictures with others, leading to stronger social relationships.
An appraisal of the existing innovative technologies
One of the most efficient and shared type of innovative technology is the Digital Manufacturing Design. Just as it has been noted to draw the attention of innovators, investors have also shifted their focus and attention to business that has adopted digital operations. The Digital Manufacturing Design has attracted different terms in different parts of the world where business occur in the digital platforms, forming the basis from which one can deduce the extent of its application. For instance, the European Union member states have termed it as “Industry 4.0” or “Industrial Internet (Bharadwaj et.al, 2013).”
Regardless of the differences in the names used to refer to the terms from different parts of the world, such labels have an ordinary meaning, as a collection of new digitally-enabled business technologies that have been adopted to enhance the process of doing things. Some of the digitally-enabled technologies include various solutions to the diverse business challenges and needs. For example, there is production equipment such as 3D Printing Technologies, Adaptive CNC Mills, robotics, smart-finished products including cars using the modern Internet of Things. In addition to the products using the internet and related technologies, there are data tools as well as analytics that have been applied across the value chains (Seror, 2013).
These technology-based techniques have created a significant change in the manner in which business occurs around the globe. Some of the changes have happened in the way in which things are being designed, manufactured, as well as overall servicing in various industrial sectors (Bharadwaj et.al, 2013). There is a new way of connection between individuals and the machine used in different industrial processes, through the digital thread in the system of the value chains. For example, the development and massive adoption of the systems of e-commerce have not only reduced the overall cost of doing business but also enhanced the profitability of the firm ventures (Barnes & Hunt, 2013). Customers may not have to travel long distances across the globe to make orders, secure purchases or make payments for goods delivered since these processes occur as simple online procedures in the digital thread built on the realities of Augmented Reality.
Methods for Collecting, Analyzing and Presenting Data Related to Digital Business
Computer-Assisted Qualitative Data Analysis Software (CAQDAS)
CAQDAS is a modern technique that offers a package and a list of software, which act as tools for qualitative research. Among the qualitative functions of this method include data transcription analysis, recursive abstraction, discourse analysis, coding and text interpretation, content analysis, as well as ground theory methodologies (Lewins, 2015). In the contemporary world of business, which revolves around technology, there has been a greater demand for a digital system of data collection, analysis, and presentation at various levels. It is mainly to the fact that it has not only become outdated to handle business data in the analogue, but it has also reduced the efficiency with which business operations occur (Barnes & Hunt, 2013).
As a method that has experienced a broad application in data collection, data analysis, and presentation, Computer-Assisted Qualitative Data Analysis Software has rendered a revolution in the data organization, management and another analytic process in digital business operations (Lewins, 2015). The vast application of the method in much digital business operations has been anchored on the fact it has manifested a wide range of advantages, such as the capacity to reduce the amount of time spend at every stage of data handling (Barnes & Hunt, 2013).
In addition to time reduction in overall data processing, the package also offers diverse tools that help to handle massive amounts of qualitative data with the utmost sense of accuracy, alongside its high rates of the flexibility of in terms of handling data with diverse nature and sources. Compared to the traditional methods based on analogue technologies, there Computer-Assisted Qualitative Data Analysis Software have enhanced validity as well as audibility (Bharadwaj et.al, 2013). Moreover, the introduction and adoption of this method of data collection, analysis, and presentation help in cost reduction since it replaces the expensive manual manpower used in handling data (Seror, 2013).
Impacts of Augmented Reality
Considering the nature of penetration of technology-based techniques of doing business in the modern world, it is possible to state that augmented reality continues to manifest its way into the society. Augmented reality has risen through the development process to become worth billion pounds. Furthermore, the extent to which it has attracted various investors such as Google, Apple, Microsoft, as well as IBM has installed deeper confidence in the possibility of its growth (Wassom & Bishop, 2015). It is possible to express utmost confidence in a stronger future existence of augmented reality. Its ability to attract the attention of major players in the world of technology is an indication of its massive potential of offering technology solutions. However, there are also a set of concerns over the potential social effects on various societies as it infiltrates its realities into the lives of users.
One of the major social impacts of the increasing rate of technology adoption particularly augmented reality is the ability to enhance the social relationships among people. The developments and resulting changes in the communication technologies have often resulted in a sense of modification in the manner in which human beings communicate with their friends and peers (Wassom & Bishop, 2015). On one hand, the ever “technology-connected” people have expressed the impossibility of living with such devices as smartphones and computers. Such a trend has been blamed for alienating people from their friends, peers, and relatives since they often spend all their time browsing and performing other tasks.
For instance, a typical technology-connected family situation is one in which every member of the family finds an engagement with a device, internet or television at the expense of bonding together as a family (Wassom & Bishop, 2015). Moreover, such a situation even worsens in family setups where its members do not find time during the day owing to other engagements such as work for parents, or school for the children. In such a family setup can only secure a little time at night before sleep, during which they can bond and catch up with each other’s lives. However, when such times are converted into technology moments, familial relationships, and at larger the societal construction of a social system get compromised (Wassom & Bishop, 2015).
As a wrap-up, therefore, the above
discussion shows that it is a statistical fact that augmented reality has
penetrated into the society, and continues to manifest the possibility of
creating a deeper sense of revolution in both businesses, and in the overall
human lifestyle. While there were initial debates regarding its potential
impact on the human society, such debates have settled over time, with most
people appraising its contribution to the overall improvement in business. It
has appeared that there are endless possibilities and opportunities in various
business ventures, which have been a source of profitability. One of the most
significant benefits in business it’s the enhanced marketing techniques that
have been enabled through the process of creating better images of the real
world. Increased sense of interconnectedness also leads to increased social
ties, which have also acted as potential sources of digital business.
References
Alem, L., & Huang, W. (2011). Recent trends of mobile collaborative augmented reality systems. New York: Springer.
Barnes, S., & Hunt, B. (Eds.). (2013). E-commerce and v-business. Routledge.
Bharadwaj, A., El Sawy, O. A., Pavlou, P. A., & Venkatraman, N. (2013). Digital business strategy: toward a next generation of insights. Mis Quarterly, 37(2), 471-482.
Geroimenko, V. (2014). Augmented reality art: From an emerging technology to a novel creative medium.
Lewins, A. (2015). Computer Assisted Qualitative Data Analysis Software (CAQDAS). Researching Social Life, 21, 411.
Mithas, S., Tafti, A., & Mitchell, W. (2013). How a Firm’s Competitive Environment and Digital Strategic Posture Influence Digital Business Strategy. Mis Quarterly, 37(2), 511-536.
Pagani, M. (2013). Digital Business Strategy and Value Creation: Framing the Dynamic Cycle of Control Points. Mis Quarterly, 37(2), 617-632.
Seror, J. (2013). Computer‐Assisted Qualitative Data Analysis Software (CAQDAS). The Encyclopedia of Applied Linguistics.
VAMR (Conference), In Shumaker, R., In Lackey, S., & International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction. (2014). Virtual, augmented and mixed reality: Applications of virtual and augmented reality: 6th International Conference, VAMR 2014, held as part of HCI International 2014, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, June 22-27, 2014, Proceedings.
Wassom, B., & In Bishop, A. (2015). Augmented reality law, privacy, and ethics: Law, society, and emerging AR technologies.
Williams, B. D., Roh, J., Tokar, T., & Swink, M. (2013). Leveraging supply chain visibility for responsiveness: The moderating role of internal integration. Journal of Operations Management, 31(7), 543-554.

