Business Ethics
Instructions:-
Part A
Proceed to a critical assessment of the Corporate Social Responsibility Report of McDonalds. In you analysis, you should critically examine the ethical environment in which McDonalds operates and consider the impact this has upon its business behaviour and performance. You can find the CSR report of McDonalds online here. Also, here the Annual Reports of McDonalds can be found here.
Part B
As Sally Bibb suggests, as a manager you have a double role. The first is to ensure that you behave ethically yourself (‘bosses have more influence that they often realize in shaping others’ behavior as people tend to consciously or unconsciously copy the boss’). The other role is that managers are responsible for making for making sure that those they manage do the right thing too. One way, moreover, to achieve that those they manage do the right thing, is through developing and introducing to employees a Code of Conduct (for more on Code of Conduct see Topic 1). In the same line of thought, this part of the assignment requires you to assume the role of a manager and develop a Code of Conduct for an organization of your Choice. This Organization may be a company you worked for in the past, or even the institution to which you are studying. In developing your Code of Conduct, you should demonstrate a critical awareness of real ethical issues that modern work placesface.
Table of Contents
Solution
Business Ethics
In the first section of this paper, the author analyses the McDonald’s corporate responsibility report and annual report with particular emphasis on the ethical environment in which the company operates and how this has impacted upon its character and performance. Key ethical areas identified in the paper include human resource aspects, environmental conservation, marketing integrity, production process, and corporate governance. It concludes that despite the challenges that continue to face the fast-food industry, McDonald’s has made great strides in carrying out their business in an ethical manner although there are still avenues for improvement.
In the second section, the author develops a code of conduct for Telecoms Network Malawi Limited (TNM) a mobile service provider headquartered in Blantyre, Malawi. The code of conduct covers areas such as individual conduct, legal compliance, health and safety, financial integrity, public policy, communication, customers, employees and the environment. The expectation on individual behavior regarding these issues has been covered.
SECTION I: Analysis of McDonald’s corporate social responsibility report
Introduction
The last few decades have seen several litigations brought against fast food enterprises on the basis of their contribution to health complications such as obesity, animal cruelty, human rights abuses among others, issues that have led to concerted efforts towards creating sustainable business models. In this section, we look into McDonald’s corporate social responsibility 2010 report and annual report with a critical analysis of the ethical environment in which the company operates and how it has impacted on its business performance and character.
Working conditions and Human Rights
Media reports have been awash with speculation over various human rights abuses at McDonald’s in regard to poor wage policies and discrimination in most of the markets that it operates in (Aljazeera America (2015). In 2001 for instance, Coalition of Immokalee Workers (US) began a campaign and subsequent go slow demanding better wages from the fast food chain. Other similar suits have been actioned against McDonald in its international network such as the ongoing Magee v. McDonald’s in which a client is suing Mcdonalds for discrimination on visually impaired people by refusing to serve them through the drive through lane.. In its corporate responsibility report, the company acknowledges the integral role played by its employees and commits to develop and retain a diverse, talented and engaged workforce. It focuses on three policy areas such as respect and inclusion, talent management and employee value proposition. This is complemented by a fair wage policy, benefits program and a profit sharing scheme. In recognition of the company’s success in ensuring fair and ethical practices in the company was voted as recognized as a ‘best and diverse employer’ in the UK, China and the Unites States (McDonalds CSR report, 2010 p. 35).
Its commitment to ethical and progressive human resource practices is also extended to all those that work in its supply chain by ensuring compliance with regard to safety and working conditions of employees. This is done through requiring direct suppliers to sign a code of conduct establishing the basic requirements for employment and practices at the workplace. This represents a commitment by all involved to extend the expectations of McDonald to all their suppliers as well (p. 31). Despite these efforts, the company still continues to face legal challenges regarding discrimination in its human resource policies (Aljazeera America (2015)
Environmental ethics
The sheer size and complexity of the McDonalds supply chain demand a lot from the environment in terms of energy requirements and carbon emissions. In order to conserve the environment and reduce its carbon footprint, the company has invested in data collection and analysis systems as well as the creation of the Global Energy Leadership Board which evaluates the global energy measurement and means of energy conservation. The company has also invested heavily in recycling technology to help conserve the environment besides the use of Green Building technology which encompasses construction and site development taking into consideration water saving, energy saving, material selection and designs. As a member of the US Green Building Council, McDonald uses advanced construction technology in order to reduce carbon footprint around the world. One of the main results of this effort is the frappe cup which is made of 40% recycled material. The use of recycling technology has been reported to reduce the quantity of landfill waste and virgin resin needed by 123 metric tons annually (McDonald’s annual report, 2016). The CSR report also indicates that over the period, the company partnered with HAVI Global Solutions, a specialty packaging company to embrace plastics thereby reducing costs by 20% while maintaining the environmental tag by reducing solid waste by 20% (McDonalds CSR report, 2010 p. 35).
Ethics in supply chain and production
According to the CSR report, McDonald makes attempts to use the best and most appropriate technology in their production process from sourcing of their raw materials to the consumer’s table. Production processes encourage minimal processing with little or no fillers or preservatives which help reduce legal exposure (The New York Times, 2002). This ensures that every step of the way from the farm to the counter is accomplished in the most sustainable and humanely as possible, with little environmental impact and considering the social and animal welfare in beef production.
McDonald’s requires its suppliers to abide by the three E’s, i.e. ethical, environmental and economic aspects of the supply chain. These values and vision for sustainable supply are shared with other stakeholders in the supply chain who are subsequently held to clear standards for safety, efficiency, and sustainability. They are also expected to extend those same requirements to their suppliers. This ensures that all stakeholders in the supply chain are collectively focused on the above three principles.
Additionally, in its commitment to a sustainable land management policy, the company endeavors to work with suppliers to ensure that agricultural raw materials originate only from legal and sustainable land resources. This enables the company to conserve biodiversity, landscapes, meet the cultural and economic needs of the communities and conserve biodiversity while ensuring a steady, high quality and an affordable supply.
Responsible and ethical marketing practices
The CSR report highlights the company’s commitment towards integrity, ethics, and responsibility in marketing practices. It has deployed the McDonalds Children Global Marketing Guidelines that provides a common set of rules governing communication to families and children with at least five major markets such as Australia, Brazil, Mexico and Canada and the US committing to Food Marketing Pledges for kids. The European market has also committed to responsible marketing principles. Although the marketing guidelines may differ from one market to the other, advertising must be true to the word and must meet the stated nutritional content and criteria.
Governance and ethics
The company’s general statement according to their governance an ethics statement is that the business is operated ethically. So critical are the values of corporate governance and ethics that they form the basis of all the corporate responsibility efforts. To attain the attendant goals, the company has created strong policies and processes and instituted strong governance structures headed by a board of directors. Besides the full board of directors, oversight of company operations is done by at least six independent board committees, including an ethics and corporate responsibility committees. Such committees work in an advisory capacity to the management of the business in regard to policy issues and strategies that affect the corporate status of the company in areas such as product safety, employee training, and diversity, employee opportunities, environment and sustainability of supply chains. Due to the significance of governance and ethics at McDonald’s and to the various stakeholders, there are a crosscutting and cross-functional and other issue-specific bodies that govern monitor and manage issues on a daily basis.
To this end, the company commits to act with integrity, in good faith, responsibly and in the interest of its stakeholders. It continues to put in measures to ensure that it achieves these roles and that the various stakeholder interests are safeguarded.
Conclusion and recommendations
Despite the challenges that continue to face the fast food industry, McDonald’s has made great strides in carrying out their business in an ethical manner although there are still avenues for improvement. This paper recommends an improvement in food technology to enhance nutritional content with reduced negative health impacts and reduction in carbon footprint for sustainable business development. The paper also recommends a global campaign on the great steps that the company continues to undertake ensuring ethical practices in all its undertakings. This goes a long way in creating a positive outlook of the company, which is necessary in its effort towards a sustainable business model.
SECTION 2: Developing a Code of Conduct
According to World customs organization (n.d), a code of conduct encompasses several areas as detailed in the figure below.
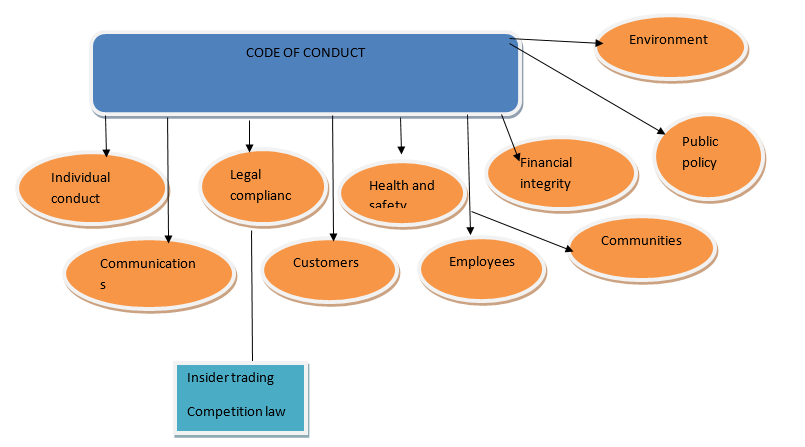
Bibbs (2010) define a code of conduct as the central policy document that outlines the requirements and expectations of every individual that works for or with the company regardless of their location. This includes employees, subsidiaries, joint ventures, directors, suppliers and other stakeholders. The consequences of not complying with the code of conduct are dire, ranging from warnings to outright dismissal and discontinuation of contracts of engagement (Lisa, 2008).
Assuming the role of a manager in this section, a code of conduct for TNM is developed. This code of conduct demands that each one of TNM stakeholders listed above is expected to:
- Behave in a manner that fosters the company ethics, taking pride in all your actions and decisions
- Understand the TNM’s way and continually apply our business principles to all your activities
- Readily speak up if in your opinion your actions or those of others are not ethical or are in breach of this code of conduct
- Ensure compliance with the rules and principles spelled out in this code of conduct and ensure fulfillment of all legal and regulatory obligations
Individual conduct
At TNM, we act with integrity, fairness, and honesty in all our engagements whether internally or externally. Any form of bribery and financial impropriety including improved giving and receiving of gifts is not tolerated. We act to avoid any contracts or any forms of engagement that may lead to, or even suggest any forms of conflict of interest between individual activities and the business (Stuart, 2005). Additionally, it’s required of every stakeholder to promote the application of all the above business principles with all suppliers and partners. Issues covered here include;
- Security of people, property, and information
This is ensured through:
- Valuing information and ensuring that it’s properly classified
- Clearing one’s desk and locking all computer screens if not in use
- Password protection at all times
- Respecting the existing laws on copyrights and other intellectual property rights
- Avoiding any forms of conflict of interest through:
- Making conscious efforts to reject any attempts to get involved in likely conflict of interest
- Disclosing such conflict or potential conflict of interest through the below mentioned channels:
- Through the respective department head, if personal conflict or potential is suspected
- Anonymously through the email: [email protected] if a colleague is involved
- Completing the relevant sections of official contracts regarding conflict of interest
- Always ensuring that you act in the best interest of the business
Legal compliance
At TNM, we comply with all the necessary legal provisions in both domestic and international jurisdictions and also ensure that our actions are in line with appropriate principles and standards of practice. We ensure specific compliance in areas such as:
Insider dealing
According to Bjorn, (2004) it’s not legal for people to gain from insider trading in most jurisdictions. This, therefore, requires each one of us to ensure that information that is not out there to the public, but which you may have access to, in the course of your engagement with TNM, is not used to inform the purchase or sale of the company stocks or securities. This particular rule applies even when your engagement with the company ends.
Competition laws
As a truly regional corporate citizen, TNM ensures compliance with the applicable laws in the protection of competition. These laws prohibit the company from making arrangements with competitors to gain undue advantage over other players in the market. To this end, TNM stakeholders should never accept, seek or discuss information that is deemed confidential with competitors. Therefore, all TNM stakeholders should:
- Have or seek to have basic knowledge of the relevant competition rules including sharing of sensitive information with competitors, price fixing, discount regimes etc.
- Always ensure to be vigilant in all business dealings with third parties with particular bias for anti-competitive practices
- Ensure compliance with the company policy on anti-money laundering, including taking robust approaches towards detection and prevention and even reporting to the management of any money laundering practices and or/ financing of terrorist activities
Health and safety
At TNM, we endeavor to protect the safety, health and the wellbeing of all stakeholders and therefore disclosure and take appropriate action in the event that information comes to our knowledge that our products or services breach international standards and accepted codes of safety guidelines and standards. This is done through:
- Ensuring compliance with policy standards on global economic sanctions
- Screening of all parties in all transactions
Everyone at TNM is expected to promote safety and responsibility in their behavior at all times. The company also commits to intervene promptly in the event that health and safety are compromised. All stakeholders are therefore expected to:
- Intervene quickly in the event of unsafe behavior
- Consider the impact of personal decisions on the health and safety of others
Financial integrity
In all our activities, our intention is to provide the best return on shareholders’ investments by making investment decisions and business relationships based on economic criteria, environmental and social considerations. All stakeholders are therefore expected to:
- Understand and apply any relevant financial policies relevant to their roles
- Ensure the best value for money spent
- Follow the company’s procurement policy manual provisions
Public policy
While we ensure to voice our considered opinions on government proposals and any other policy matters that affect our business, we do not lobby or make contributions, donations or interventions in political matters. All stakeholders are therefore expected to:
- Ensure compliance with the laid down brand guidelines and communications standards
- Report in case of suspected misuse of trademarks and intellectual property rights
- Never to make any communications on behalf of the company unless you are authorized to do so in consideration of the Public and Media Relations Policy Standard.
Communications
At TNM, communication is open, transparent and within the bounds of confidentiality. Confidential information is therefore protected from any form of improper use and therefore authorized communication is only limited to individuals in carrying out their work. This, therefore, means that:
- We should all ensure that any communication in and out of the company is professional, timely and where necessary, approved
- We should all act professionally especially when in TNMs branded uniform, vehicle or attending an event on behalf of the company
- Never make a statement that is likely to have a negative or unintended impact on the company
- Keep any information that is confidential as such
Customers
At all times, we value our customers and do all that is possible to safeguard any customer information in our possession. To this end we ensure:
- Openness and honesty by communicating clearly to our customers on all our actions and how they may impact their privacy and ensure that all actions reflect our words
- We provide our customers with the ability to make meaningful choices about their privacy by designing our products with privacy components inbuilt
- Presented with a choice between our customer’s privacy and other obligations, we ensure to reduce their exposure as much as practicable
- We comply and support the development of privacy laws, policies and regulations in all our jurisdictions
Vendors
We value our suppliers and ensure that all agreements with our vendors are adhered to in a reasonable manner. To this extend, we;
- Maintain a vendors register for all vendors associated with the company
- Ensure all vendors are given a fair chance to do business with the company
- Ensure payments to vendors are done as per stipulated agreements
- Demand of all our vendors, the highest level of professionalism in the conduct of their business with the company.
Employees
We ensure that all our relationships with employees reflect our commitment to respecting and upholding human rights. We ensure:
- Compliance with the company’s business principles and policy standards
- Act in a fair and respectful manner towards all
- Challenge any form of discriminatory behavior
- Base any recruitment decisions solely on merit
- Employees do not accept gifts or give any favors to vendors and other stakeholders outside of their professional engagement with the company
Communities and society
TNM endeavors to understand our local communities and respond to their concerns that they may have in relation to our activities. To achieve this, we encourage you to:
- Never engage in drugs and substance abuse, and never to work under the influence of such drugs
- Report any concerns about colleagues’ use of drugs
- Be sensitive to the plight, needs and listen to concerns that people may have about TNM’s business
- Get involved in the activities of the local communities through our foundation
Environment
The TNM fraternity commits to minimizing our carbon footprint by embracing green technology in most of our activities. This demands that we all:
- Become familiar with any applicable environmental laws, policies, and regulations
- Reduce wastage
- Insist of recycling our waste products
- Avoid unnecessary travel
- Walk or even use public transport as much as possible
- Consider car sharing with colleagues to reduce carbon emissions
- Consider the environment in all purchasing decisions
Conclusion and recommendations
On TNM’s code of conduct, it’s concluded that strict adherence to the provisions of the code of conduct is key to harnessing the benefits of that proprietary document. Such benefits will transcend the company’s bottom line, but will also enhance its sustainability by benefiting the society and environment within which the company operates. The existence of this document is however, not enough. Management must take it upon itself to carry out regular campaigns to sensitize staff and other stake holders on the importance of a code of conduct and ensure that each and every one is aware of the provisions of the document, and that its being adhered to in the day to day operations of the company. Additionally, establishment of an ethics department/committee that is responsible for the administration and education on the code of conduct is necessary in ensuring accountability and strict adherence to it. Its also necessary to frequently update the code of conduct to reflect the changing trends in the modern business ethics environment.
References
McDonald’s Corporation Worldwide Corporate Social Responsibility 2010 Report. Retrieved from: http://corporate.mcdonalds.com/content/dam/AboutMcDonalds/Sustainability/Sustainability%20Library/2010-CSR-Report.pdf
Lydersen, K (2005) McDonald’s vs. the Tomato Pickers: The fast-food giant tries to appease migrant farmworkers while doing everything possible to keep its labor costs dirt-cheap. http://www.alternet.org/story/29832/mcdonald%27s_vs._the_tomato_pickers
Mcdonald’s Corporation Annual Report (2016) http://corporate.mcdonalds.com/content/dam/AboutMcDonalds/Investors/2016%20Annual%20Report.pdf
The New York Times (2002) Teenagers’ Suit Says McDonald’s Made Them Obese. Retrieved from http://www.nytimes.com/2002/11/21/nyregion/teenagers-suit-says-mcdonald-s-made-them-obese.html
Aljezira America (2015) McDonald’s sued over allegations of discrimination. http://america.aljazeera.com/articles/2015/1/22/mcdonalds-sued-over-allegations-of-discrimination.html
Bibb, S (2010) The Right Thing: An Everyday Guide to Ethics in Business. John Wiley & Sons
Stuart, C.G. (2005). Ethics Codes and Codes of Conduct as Tools for Promoting an Ethical and Professional Public Service: Comparative Successes and Lessons
Telekom Networks Malawi Limited. Available at: https://www.tnm.co.mw/
Lisa H. N. (2008). Culture Is the Key to Employee Adherence to Corporate Codes of Ethics. Journal of Business & Technology LawL. 449 (2008) Available at http://digitalcommons.law.umaryland.edu/jbtl/vol3/iss2/14
World Customs organization (n.d). Model Code of Ethics and Conduct. http://www.wcoomd.org/-/media/wco/public/global/pdf/topics/integrity/instruments-and-tools/model-code-of-ethics-and-conduct.pdf?la=es-ES
Bjorn, A. (2004). Bringing business ethics to life: Achieving corporate social responsibility. California: American Society for Quality.

