Part A: Quality improvement/change intervention proposal: [3,000 words, 75% of total grade; assesses learning outcomes 1 – 4] Prepare an evidenced based proposal for a quality improvement/change intervention to be implemented in YOUR OWN HEALTHCARE ORGANISATION using the following headings:
1. Introduction [Brief background to quality improvement/change interventions, introduction to your subject matter and the contents of your assignment (“signpost”). Reference to the evidence-base will be useful…]
2. The importance of evaluation, research and measurement [A critical, evidence-based discussion investigating the importance of evaluation, measurement and research in managing healthcare and/or quality and safety in healthcare.]
3. Problem description [Nature and significance of the local, organisational problem – this could be meaningful disruption, failure, inadequacy, distress, confusion or other dysfunction in your organisation that adversely affects patients, staff or the system as a whole, or that prevents care from reaching its full potential. Reference to the evidence-base will be useful…]
4. Available knowledge [Summary of what is currently known about the problem, including relevant previous studies – this is a critical discussion of the evidence-base in the quality improvement/change intervention area (literature review!). Remember to identify and critique conflicting evidence and draw appropriate conclusions.]
5. Rationale and context [An explanation of why you have chosen the quality improvement/change intervention, why it will work and why it is both sustainable and replicable. The context is the physical, social and cultural factors that “makes” your organisation what it is (e.g. external environmental factors, organisational dynamics, team work/collaboration, resources and leadership) and your interpretation of these factors that could affect the effectiveness and generalisability of intervention. Reference to the evidence-base will be useful…]
6. Objectives for the proposed quality improvement/change intervention [How you will achieve the proposed quality improvement/change intervention – S.M.A.R.T. statements defining measurable outcomes. These can be “listed” in your assignment. Reference to the evidence- base will be useful…]
7. Study, measures and evaluation for the proposed quality improvement/change intervention [Approach chosen for critically analysing and assessing the impact of the quality improvement/change intervention, including your approach to ensure the outcomes will be due to the intervention. This should include the measures chosen for studying the processes and outcomes of the intervention, including the rationale for choosing them, operational definitions, validity and reliability, approach to ongoing assessment and methods to ensure the completeness and accuracy of data collected. Reference to the evidence-base will be useful…]
8. Ethical considerations [Any ethical aspects of implementing and studying the proposed quality improvement/change intervention and how these will be addressed, potentially including formal ethics review and conflicts of interest. Reference to the evidence-base will be useful…]
9. Limitations [Factors which could limit the proposed quality improvement/change intervention’s generalisability, internal validity (confounding, bias or imprecision in design, methods, measurement or analysis) and approaches to minimise such limitations. Reference to the evidence-base will be useful…]
10. Conclusion [A brief summary of what has been discussed, a suggested course of action and a statement which summarizes your main point or conclusions of the arguments you have made] Part
B: Reflection: [1,000 words, 25% of total grade; assesses learning outcomes 5] Beginning with your prior experience and understanding, critically reflect on the key learnings you have achieved during Module 3 “Evaluation, Measurement & Research” and identify how you can apply these key learnings to your area of practice. [Your reflection must be structured using an established reflective model e.g. Gibbs Reflective Cycle and references are not mandatory]
a. Critically discuss the importance of evaluation, measurement and research in managing healthcare and/or quality and safety in healthcare.
b. Critically evaluate research reports relevant to your field of study.
c. Critique key approaches to evaluation, measurement and research (such as performance indicators, audit and quantitative and qualitative research methods).
d. Critically discuss how to evaluate quality improvement/change in a healthcare organization.
e. Demonstrate an understanding of critical reflection on key concepts around evaluation, measurement and research.
Solution
An Evidence-Based Proposal for Quality Improvement/Change Intervention
Introduction
According to Hughes (2008), quality improvement is a multidisciplinary, systems-focused, and a data-driven, evidence-based approach of understanding and improving effectiveness, efficiency, and the reliability of health processes and the outcomes of care. As the healthcare sector focuses on the elimination of disease, the improvement, promotion, and protection of the health and wellbeing of every citizen, the need for the development of more efficient and reliable healthcare systems and processes is undeniable. Every healthcare organization must focus on the creation of an effective platform for the delivery of quality and safe health care services through the development and implementation of efficient programs, processes, and healthcare systems. The integration of the evidence-based care and medicine with the quality improvement (QI) serves a significant role in the enhancement of quality and safety in the delivery of health care. This study will focus on the development of an evidence-based proposal for quality improvement/change intervention in the ABC health organization. The proposal will further outline the importance of processes such as evaluation, research, and measurement, and ethical considerations through an extensive review of literature.
The Importance of Evaluation, Research and Measurement
The QI process is designed for the improvement of the standards of delivering preventive, diagnostic, rehabilitative, and therapeutic measures in order to maintain, restore, and raise the quality of care. The method guarantees improved health care by focusing on implementing measures and strategies that enhance the effectiveness of different health systems and approaches. However, as Carroll (2013) asserts, the improvement of the quality of care demands the integration of multiple other techniques. Research, evaluation and measurement play an essential role in the enhancement of effectiveness and efficiency in healthcare systems, programs, and processes. As such, there is a dire need for every organization to focus on the effective implementation of evaluation and measurement techniques while engaging in constant research. Though the ABC healthcare facility seems to understand the importance of research, evaluation, and measurement, the organization must implement measures and strategies that focus on enhanced application and integration of the three aspects in medical care.
The element of measurement is important in the promotion of quality improvement/change in healthcare organizations. The ABC organization recognizes the importance of quality measurement in the improvement of quality within the organization. The implementation of the measurement aspect determines and demonstrates the effectiveness of the improvement efforts in bringing about positive change in the organization (Grimmer, et al., 2014). The organization focuses on the determination of whether the adopted strategies and efforts to improve quality trigger change in the desired direction. The strategies and measures are targeted towards the enhancement of quality delivery and the promotion of patient safety and satisfaction. In this regard, measurement determines whether the measures and strategies work towards the achievement of the set objectives or whether they contribute to unintended outcomes/results in the various parts of the systems, processes, or organizational programs. Moreover, it seeks to determine whether there is a need for additional efforts that can bring change which assures quality improvement (Hughes, 2008).
Quality measurement involves the application of rigorous, systematic, and quantifiable techniques focusing on the structures and processes of care that demonstrate a relationship to positive health care outcomes and remain under the control of the healthcare system. The rationale for quality improvement measurement is the belief that excellent performance in health care delivery reflects good-quality practice and that the comparison of performance encourages improved and better performance (Hughes, 2008). As such, quality improvement measurement is critical for the enhancement of performance and improvement of the organizational programs and processes that cause improved quality. Moreover, measuring quality improvement determines the areas that need improvement and places an organization in a better position for the identification of the most effective strategies that can be applied for enhanced quality in the delivery of evidence-based care. Existing evidence reveals that healthcare facilities that implement quality improvement measurement record increased and continuous QI (McLaughlin, Johnson, & Sollecito, 2012). Thought he ABC healthcare organization measures quality improvement, it is important to implement more effective measurement techniques for enhanced quality care delivery.
Research is a critical component in any healthcare organization. Its integration in the process of quality improvement in care delivery plays a crucial role in the advancement of the health and wellbeing of patients and staff. Healthcare institutions must constantly engage in research to outline the most effective processes, efficient systems, and sustainable programs. Research makes the implementation of evidence-based practice/medicine possible by enabling health care providers to identify new approaches and integrating their expertise and existing knowledge in the provision of services. Most importantly, the application of research results in patient care plays a critical role in the improvement of efficacy of care and thus the improvement of the quality of care (Stevens, 2013). Research results also make it possible for the implementation of evidence-based medicine which in the recent past has led to a substantial improvement of quality of healthcare. Through research, the health sector identifies new and more effective treatments and upon deep analysis applies them in the provision of health care services. The process means that old approaches and treatments that prove inefficient, costly, and ineffective are abandoned. The integration of QI with research offers a rational, efficient, and significantly fast methods that support the incorporation of new knowledge to practice environments and the creation and testing of innovations targeted towards the improvement of systems of care delivery (Margolis, Provost, Schoettker, & Britto, 2009).
| Characteristic | QI Measurement | Research |
| Goal | Improve care, identify | Find new knowledge |
| Scope | Focuses on specific systems, processes, and programs | Broad and generalized, covering different studies and populations |
| Design | Controlled by evidence | Focuses on process |
| Results | Results are shared and used within the facility for improvement and change | Results are widely shared through research journal, in conferences, and through different media for evidence-based care |
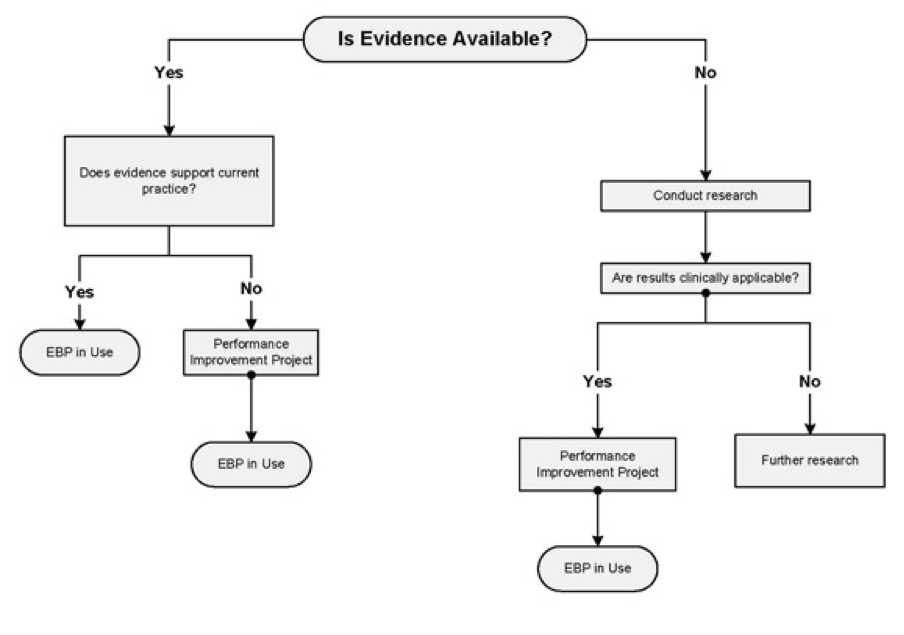
Apart from the integration of research with, and the measurement of QI, evaluation is another critical aspect of QI. Evaluation involves the determination of the availability of evidence in practice. The importance of evaluation is that it allows the organization to conduct research where evidence does not exist and to ensure the clinical applicability of the research results. Where the results are inapplicable, the evaluation allows further research or the implementation of a performance improvement project where the results are applicable in care. These processes make sure that the healthcare organization can effectively apply evidence-based practice in the delivery of care. The application of the EBP enhances effectiveness and thus improves the quality of care. On the other hand, where evaluation depicts that the evidence derived from research does not support the current practice, the organization engages in a performance improvement project that like in the aforementioned case leads to the applicability of the EBP (Muller, 2015). All in all, the process enhances QI thus making evaluation a critical component.
Problem Description
Different factors limit the process of delivering health care and thus lead to numerous adverse effects of the patients, the staff, and the organization in general. While the ABC health facility focuses on constantly improving the quality of care, infections and healthcare acquired conditions remains significantly high. Various interventions can be adopted and implemented for the alleviation of the clinical risk, infection control, and the promotion of health and safety. However, the promotion of hand hygiene and handwashing awareness would play a significant role in the elimination of infections, the promotion of health, the safety and wellbeing of patients, staff, and the society (Kavaler & Alexander, 2014). As a multidisciplinary approach, QI faces a significant challenge in the healthcare setting. However, it remains of critical importance in the way it improves efficiency, performance, effectiveness, and safety within the healthcare organization. The ABC records different cases of medical and care errors that limit quality in the provision of care. Healthcare acquired infections and conditions remain a major challenge due to the inefficient programs and the medical and care errors. The ABC continues to record cases of the infections and conditions. Therefore, it is important for the organization to implement hand hygiene program that focuses on improving health and safety by controlling and managing infections. One sure way of ensuring the achievement of the abovementioned aims is through QI utilizing evidence-based intervention approaches. The approaches should focus on the identification of inefficiencies, ineffectiveness, preventable errors, and all other issues and risks associated with ineffective programs.
Literature Review
Numerous studies discuss the importance of the implementation of effective QI interventions in the healthcare setting. Portela, Pronovost, Woodcock, Carter, and Dixon-Woods (2014) and Solberg, Mosser, and McDonald (1997) argue that the implementation of such interventions plays an important role in the promotion of the major objective of every healthcare facility, which is the promotion of the health and well-being of patients and the staff. While this is the case, Kavaler and Alexander (2014) and Carroll (2013) support the authors but add that the implementation of an efficient quality improvement/change intervention places the healthcare sector at an elevated ground for fighting disease and eliminating conditions acquired in healthcare organizations. Most importantly, Kavaler and Alexander (2014) assert that the improvement of the quality of care enhances the patient’s quality of life, reduces risks in the organizations, and promotes the wellbeing of not only the patients and staff but also of the society. In the recognition of the importance of quality improvement, most authors posit that different organizations have adopted and implemented different interventions focusing on improving quality care and promoting and protecting the health and wellbeing of each within the society.
According to the CDC (2015), most hospitals have made impressive strides in the improvement of patient safety and the quality of care. However, according to Conway (2013), one in every twenty patients is infected while in a hospital. Cases of hospital-acquired conditions/infections remain high despite the efforts implemented in the past to counter them. Different hospitals continue to record infections and conditions developed while the patients are in the hospital and under care. Considering this, different authors argue for the need to ensure effective implementation of interventions that focus on alleviating such issues, improving patient safety, and enhancing QI. The improvement of patient safety would play a significant role in the reduction of HACs and infections. The CDC reports an increasing commitment by hospitals in the elimination of HACs and infections and states that such commitment has resulted in the reduction of the conditions/infections. However, Krein, Kowalski, Hofer, and Saint (2012) argue for the need to improve efforts to reduce HACs and that many healthcare facilities do not seem to apply effective interventions for the alleviation of the issue.
Moreover, other studies depict that risks and ineffective risk management techniques have contributed greatly towards reduced quality of care (Martin, Williams, Haskard, & DiMatteo, 2005). The risks place the staff, patients, and the society in general at risk for the development of different health care concerns (Nelson & Baptiste, 2004: Vincent, 2010). The need for QI and the enhancement of safety in healthcare organizations is undeniable. The government must work towards the assurance of improved quality of care and safety. The implementation of efficient interventions and programs for quality improvement/change would cause a significant improvement in the healthcare system’s proficiency and profitability. According to Kavaler and Alexander (2014), the different measures such as patient and staff education on hygiene and different ways of minimizing the risk of exposure and development of various conditions may enhance safety and reduce HACs and infections. Moreover, more needs to be done by arguing that education has consistently being in use over the years. The author asserts that there is a need to integrate new techniques into the delivery of the education such as the use of posters that offer guidelines for handwashing and other measures (CDC, 2014). Most importantly, there is a need for every healthcare organization to adopt and implement an effective risk management program.
According to the CDC and the WHO, hand hygiene is the most significant approach for the elimination and control of healthcare acquired infections and conditions. Other researchers support the argument by stating that the implementation of efficient hand hygiene programs would help save lives by reducing infection risks (Mathur, 2011: Rhinehart & Friedman, 2006). Moreover, the CDC (2015) and WHO (2007) support the argument that handwashing can save lives in the healthcare setting and in the society and reduce and control infections significantly.
Objectives
- To alleviate cases of hospital-acquired conditions.
- To effectively control and manage infection risks through an effective hand hygiene program, and
- To integrate new research, treatment options, and healthcare systems and processes efficiently in care.
Intervention Measures
The implementation of an efficient intervention program for quality improvement/change would cause a significant improvement in the healthcare system’s proficiency and profitability. First, the organization should focus on the creation of an effective risk management program that identifies, analyzes, and develops efficient risk treatment measures, and further evaluates the risks to avoid the risks. The program should cover areas such as patient safety, infection control, and management of medical equipment, fire prevention, and management information, hazardous wastes and disaster preparedness among others. The effectiveness of the risk management program will lead to improved patient and staff safety and enhanced quality of care. All these will work towards QI, which will lead to enhanced patient health, quality of life and societal livelihood.
The integration of hand hygiene in the management and control of infections and related risks would attach effectiveness and efficiency in the process. The organization should focus on the development of its hygiene program to improve the quality of care, the health, and safety of patients and staff (WHO, 2007). During the development of the hand hygiene program, the organization should invest on educating patients and staff and creating awareness on the issue of infections and healthcare acquired conditions that develop due to poor hand hygiene. Focusing on the implementation of specific strategies such as hand washing, use of critical protective equipment such as goggles, gloves, and gowns among others would play a major role in the advancement of quality health care.
The hand hygiene program should involve education for the creation of awareness on its importance in the control of infections. The organization must utilize pamphlets and posters that demonstrate how to rub hands for hand hygiene and the most effective way of handwashing and taking care of hands for health care providers and patients. The posters should be placed in the different joints that provide handwashing equipment to serve as a reminder every time an individual wants to wash their hands (Kavaler & Alexander, 2014). Additionally, effective hand care should guide providers to take care of their hands by regular use of protective hand cream, avoiding artificial fingernails, avoiding routine use of soap and water in handwashing immediately after or before using an alcohol-based handrub among others (WHO, 2007). The diagrams below demonstrate the process of handwashing and rubbing hands during the process.
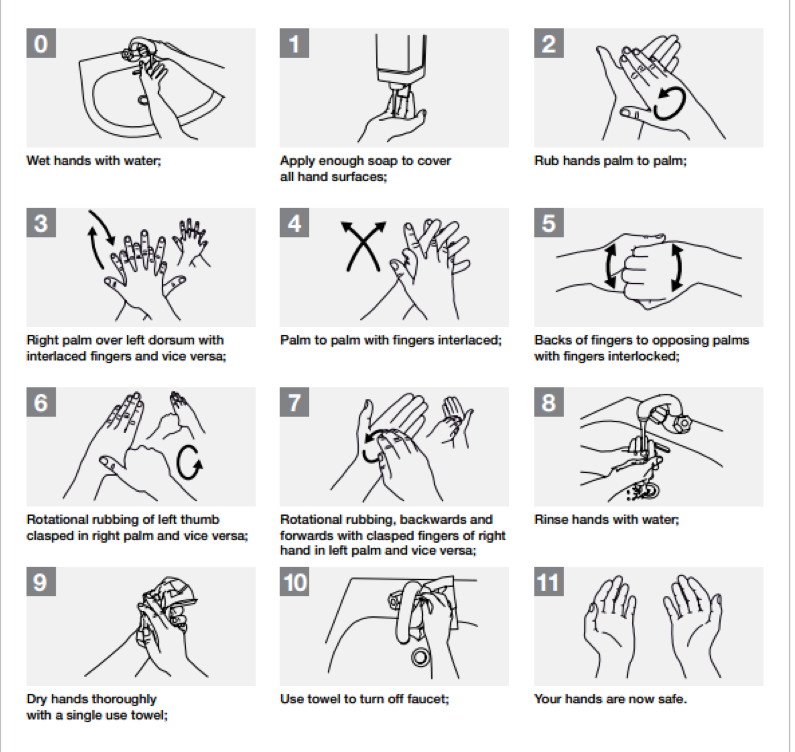
Most importantly, the hand hygiene program should make certain that the health care providers are efficient in practicing hygiene. The staff should wash hands before touching a patient, before clean/aseptic procedure, after exposure to body fluids, after touching a patient and after touching patient surroundings. By washing hands, the providers protect the patients from colonization and against exogenous infection by germs carried on their hands. Additionally, the process protects the health care providers from colonization with patient germs and from infections.
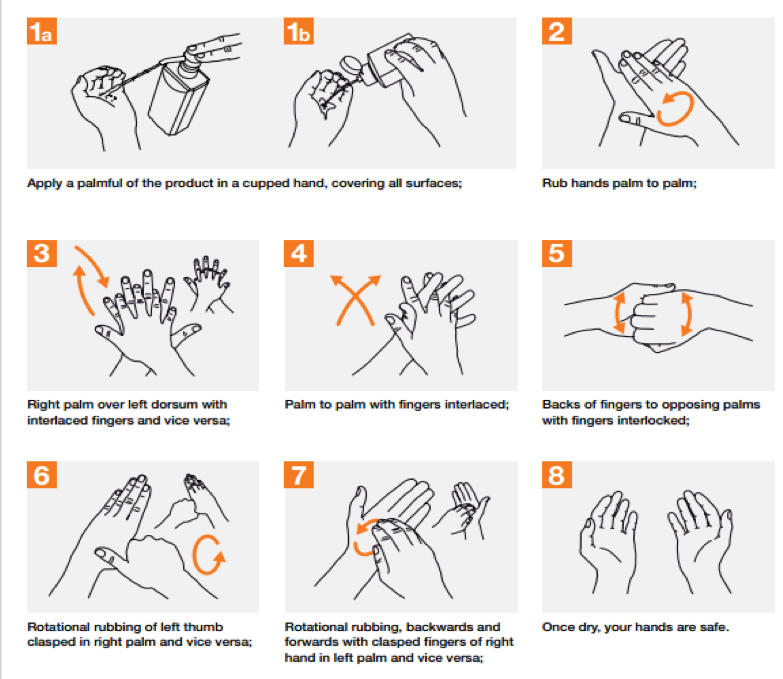
Also, the organization should make sure to adhere/practice to evidence-based medicine, implement effective data and information systems, and use surveillance systems for boosting safety and quality improvement through identification of the HACs and infections and the minimization of the possibility of patient harm. The implementation of effective systems for health records, patient, and staff information reduces cases of HACs by centralizing the data and averting avoidable infections. Additionally, evidence-based healthcare practices active surveillance limit the cases of infection in patients help the management in the development of safe and effective intervention measures (Murni, Duke, Kinney, Daley, & Soenarto, 2015).
Rationale and Context
An effective hand hygiene program in the organization will serve an important role in the elimination of infections and conditions acquired in healthcare facilities. Thousands of patients across the world die from HACs and infections. As such, the intervention, which focuses on alleviating cases of infections in the organization is the most significant intervention for the improvement of quality care. According to the WHO (2015), hands are the main and most effective pathway for the transmission of germs in the processes of health care delivery. Therefore, hand hygiene is an important measure for the prevention of healthcare-associated infections. The choice of the intervention was made based on its effectiveness in the elimination of infections and the improvement of quality in health care. That the intervention involves the patients, staff, and the society and involves considerably low capital input makes it easily applicable. Additionally, it guarantees positive change that involves improved quality over the long-term making it sustainable. With management, staff, and patient cooperation, the implementation of the intervention would ascertain change. However, lack of cooperation from the different parties may challenge its application.
Ethical Considerations
There is a need for ethical consideration even in the implementation of strategies that may improve the quality of care, promote the health, safety, and the quality of life of the patients and staff. In the implementation of any intervention, the organization must understand and respect diversity to avoid misunderstandings or infringement on other patient rights. For instance, the interventions must be flexible to prevent the violation of patients’ right to religious beliefs, the right to live, information, and efficient communication. Moreover, even with the application of the effective surveillance and data and information systems, the organization must recognize the patients’ right to privacy. Also, in the implementation of the different interventions targeted towards the improvement of quality in the delivery of care and the minimization of costs, there is a need for the management to ensure that the rights of the patient are not abused. For instance, in the implementation of ‘do-not-resuscitate’ (DNR), the organization should ensure that it is in accordance with the will of the patient and that relatives or family members do not misuse such laws more so where the patient cannot participate in decision-making (Kaldjian & Broderick, 2011).
Limitations
The implementation of the evidence-based QI and change intervention measures may come with various limitations. The different interventions have costs and play varied roles towards the enhancement of quality in the delivery of care. For instance, the implementation of interventions such as the promotion of patient education and support, the integration of efficient data and information systems, the availability of essential protective equipment, adherence to EBP and care, and the development of effective surveillance in the ABC healthcare organization will demand a high input in terms of financing and other costs that may include opportunity costs. Moreover, another critical limitation will be the inability to determine which of the intervention works best and is the most effective (Redle & Atkins, 2012). In the case of ABC, the challenge will be the identification of the intervention(s) that work most effectively for prioritization under particular circumstances. For instance, even when patient education may be effective in the elimination of HACs, there is actually no guarantee that the patients will implement the information received. As such, the interventions may pose different challenges in the implementation but their integration in the processes, programs, and systems of the organization will guarantee immense development and quality improvement.
Conclusion
As medical errors remain rampant in healthcare organizations and within the sector in general, there is a need for quality improvement/change. The ABC organization must focus on the establishment of organizational programs, processes, and systems that diligently tackle all issues that limit the delivery of quality care and threaten the safety of patients. This would require the implementation of effective strategies and measures. The achievement of success in the process would demand the integration of different techniques and approaches. In the control and elimination of infections, the organization must implement an effective hand hygiene program. The program will enhance health, reduce infections and associated risks and promote safety for the patients and health care providers. Moreover, there is a need to integrate intervention measures including an integrated risk management program, efficient analytic techniques, and effectively implemented programs. The programs may include effective data and information systems, surveillance, and availability of protective equipment among others.
Part B – Reflection: Applying the Gibbs’ Reflective Cycle
Description
Quality improvement interventions play a significant role in the enhancement of the quality of care delivered in a healthcare organization. In the identification and implementation of effective interventions, several elements are critical. There is a need for extensive research, measurement and evaluation of existing processes, healthcare systems, and programs/approaches. Before studying this unit and prior to the conduction of this research, I had limited information and knowledge on the importance of research, measurement and evaluation in the improvement of quality of care. However, in the course of the study, I developed substantial knowledge on the matter. The three aspects are of great importance in the management of healthcare. The application of the trio in the management of a healthcare organization places the organization and its management in a better position for quality improvement, and guarantees enhanced safety for the patients and staff. The processes thus improve patient health and safety while minimizing risk in the delivery of care and promising the healthcare providers safety in the course of their duties. Moreover, I identified healthcare-acquired infections/conditions as a major challenge in the delivery of quality care.
Feelings
The rate of healthcare-acquired infections in the ABC organization was alarming and the identification of ineffectiveness in the programs employed for improving quality equally disturbing. In the management of quality and safety in healthcare, research plays an important role in the identification of new approaches, treatments, and techniques for the improvement of quality. I felt there was a need for the organization to implement effective research, measurement, and evaluation techniques. Moreover, that infections impact greatly on the patients and organization’s staff, I felt there was a need to apply an effective intervention for the reduction of HACs and infections and the improvement of quality in the delivery of health care. Also, in my understanding, the measurement of QI is an essential process that will promote quality service delivery in healthcare organizations. The application of rigorous, systematic and quantifiable techniques in the process will determine areas that need improvement and trigger change within an organization. The change experienced as a result of measurement of QI in an organization will be positive and will cause improved quality. Evaluation
The organization should critically evaluate quality improvement to ensure the promotion of health care and the safety of patients and staff. The evaluation of QI should include exhaustive processes based on scientific evidence and sufficient research (Murni, Duke, Kinney, Daley, & Soenarto, 2015). The evidence should reveal the ability to be easily measured and compared with existing knowledge and information within the control of the organization. Additionally, patient satisfaction can be employed in the evaluation of the effectiveness of the interventions integrated into the systems and processes of the organization. The organization may apply the surveillance systems, the efficient data and information systems, and databases and item-by-item measurement as evaluation techniques (Hawes, 2014). Of greater importance, the organization should ensure efficient implementation of the hand hygiene program in order to minimize cases of infections and trigger QI. In the evaluation of the effectiveness of the program, techniques would outline the applicability and effectiveness of the interventions and its contribution towards the improvement of quality in the organization. The ability of the techniques to measure and incorporate research results in the evaluation to articulately pinpoint the effectiveness of the intervention would ensure efficiency in the whole process.
Analysis
In the implementation of research, measurement, and evaluation, an organization must apply efficient approaches to ascertain reliability and effectiveness. For instance, while performance measurement and indicators demarcate the extent of success of an organization, they do not always depict the situation with the required accuracy levels due to the influence of other factors. Cost, revenue, and profitability as performance indicators may not reveal the effectiveness of the interventions because they are affected by other variables. However, their application may be used to measure effectiveness of costs and the reduction and management of costs to ensure increased profit efficiency and consequent high revenue. Moreover, other approaches such as methods, valuing, and utilization is essential in the promotion of the effectiveness (Bowen, 2015). For instance, the organization’s application of qualitative methods instead of quantitative may promote testing, transferability, and applicability of knowledge. Also, valuing and utilization reveal the need for added information and research, the necessity for policy and the integration of knowledge. The application (or lack of it) of the different approaches in the research, measurement, and evaluation in the ABC would enhance effectiveness in the organization.
I believe there is a need for more effort in the promotion of QI in the organization. Though the ABC healthcare organization has in the past invested heavily in research and applied measurement and evaluation techniques, there is a need for increased effort in the processes. Evaluation in the organization has revealed its importance in the past through the creation of an effective platform for efficient application of evidence-based practice/care. That the process analyzes the effectiveness of evidence-based practice and makes an observation on the applicability of the research results in the practice makes it critically important for health care. The evaluation of different research results from the ABC research ensures the determination of the possibility of the results to develop new and effective treatments, processes, and systems for improved efficiency, effectiveness, and performance in the delivery of care in the organization. If the organization implements the outlined intervention measure, it will achieve significant success in the alleviation of infections and the management of infection risks. However, the lack of efficient measurement and evaluation interventions in the organizations may make it difficult for it to implement relevant research results. As such, there is a need for ABC to focus on constantly improving its processes and systems through the implementation of efficient interventions.
Conclusion
In consideration of the seriousness of the issue of quality health care and the concerns that arise when low-quality services are delivered, I believe the ABC must implement the hand hygiene intervention with immediate effect. The organization should build on the existing program by availing more equipment, creating awareness, educating patients, and motivating staff. The installation of posters and the distribution of pamphlets on the importance of hand hygiene would be critical. Further, I strongly feel that the integration of other interventions that influence the implementation of hand hygiene directly or indirectly should be implemented for effectiveness in the process.
Action Plan
As a part of the ABC, I will focus on the creation of awareness on the importance of quality improvement, ensure that I observe the hand hygiene guidelines and motivate colleagues and staff to follow them to the latter. Moreover, I will cooperate with the management and staff members in teamwork and in the promotion of the objectives of the intervention. Additionally, I will make sure I manage the available resources well and implement the set organizational strategies to guarantee improved quality in health care provision.
References
Bowen, S. (2015). A Guide to Evaluation in Health Research. Retrieved from Canadian Institute of Health Research: www.cihr-irsc.gc.ca/e/45336.html
Carroll, R. (2013). Risk Management Handbook for Health Care Organizations. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass – A Wiley Imprint.
CDC. (2014, May 1). Hand Hygiene Basics. Retrieved from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: http://www.cdc.gov/handhygiene/Basics.html
Conway, P. (2013, September 24). U.S. Efforts To Reduce Healthcare-Associated Infections. Retrieved from U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) : http://www.hhs.gov/asl/testify/2013/09/t20130924.html
Grimmer, K., Lizarondo, L., Kumar, S., Bell, E., Buist, M., & Weinstein, P. (2014). An evidence-based framework to measure quality of allied health care. Health Research Policy and Systems 12 (10).
Hawes, R. (2014). Ensuring quality of care is safe. Nursing & Residential Care 16 (11), 653-653.
Hughes, R. G. (2008). Tools and Strategies for Quality Improvement and Patient Safety. In R. G. Hughes, Patient Safety and Quality: An Evidence-Based Handbook for Nurses. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US).
Kaldjian, C. L., & Broderick, A. (2011). Developing a policy for do not resuscitate orders within a framework of goals of care. Joint Commission Journal on Quality and Patient Safety/ Joint Commission Resources 37 (1), 11-19.
Kavaler, F., & Alexander, R. S. (2014). Risk management in healthcare institutions : limiting liability and enhancing care (3rd Edition ed.). Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Krein, S. L., Kowalski, C. P., Hofer, T. P., & Saint, S. (2012). Preventing hospital-acquired infections: a national survey of practices reported by U.S. hospitals in 2005 and 2009. Journal of General Internal Medicine 27 (7), 773-779. doi:10.1007/s11606-011-1935-y
Margolis, P., Provost, L. P., Schoettker, P. J., & Britto, M. T. (2009). Quality improvement, clinical research, and quality improvement research–opportunities for integration. Pediatric Clinics of North America 56 (4), 831- 841.
McLaughlin, C. P., Johnson, J. K., & Sollecito, W. A. (2012). Implementing continuous quality improvement in health care : a global casebook. Sudbury: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Muller, B. (2015). Evidence, Research and Quality Improvement In Clinical Practice. Nursing Excellence e-Edition (10).
Murni, I. K., Duke, T., Kinney, S., Daley, A. J., & Soenarto, Y. (2015). Reducing hospital-acquired infections and improving the rational use of antibiotics in a developing country : an effectiveness study. Archives of Disease in Childhood 100 (5) , 454-459.
Portela, M. C., Pronovost, P. J., Woodcock, T., Carter, P., & Dixon-Woods, M. (2014). How to study improvement interventions: a brief overview of possible study types. BMJ Quality & Safety .
Redle, E. E., & Atkins, D. (2012). The applicability of quality improvement research for comparative effectiveness. Implementation Science 8 (1), 1-6.
Solberg, L., Mosser, G., & S, M. (1997). The three faces of performance measurement: improvement, accountability, and research. The Joing Commission Journal on Quality Improvement 23 (3), 135-147.
Stevens, K. (2013). The Impact of Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing and the Next Big Ideas. The Online Journal of Issues in Nursing 18 (2), Manuscript 4.
The Joint Commission. (2016). 2016 National Patient Safety Goals. Retrieved from The Joint Commission – National Patient Safety Goals: http://www.jointcommission.org/standards_information/npsgs.aspx

